SMG6 regulates DNA damage and cell survival in Hippo pathway kinase LATS2-inactivated malignant mesothelioma
- PMID: 36335095
- PMCID: PMC9637146
- DOI: 10.1038/s41420-022-01232-w
SMG6 regulates DNA damage and cell survival in Hippo pathway kinase LATS2-inactivated malignant mesothelioma
Abstract
Many genes responsible for Malignant mesothelioma (MM) have been identified as tumor suppressor genes and it is difficult to target these genes directly at a molecular level. We searched for the gene which showed synthetic lethal phenotype with LATS2, one of the MM causative genes and one of the kinases in the Hippo pathway. Here we showed that knockdown of SMG6 results in synthetic lethality in LATS2-inactivated cells. We found that this synthetic lethality required the nuclear translocation of YAP1 and TAZ. Both are downstream factors of the Hippo pathway. We also demonstrated that this synthetic lethality did not require SMG6 in nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD) but in regulating telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT) activity. In addition, the RNA-dependent DNA polymerase (RdDP) activity of TERT was required for this synthetic lethal phenotype. We confirmed the inhibitory effects of LATS2 and SMG6 on cell proliferation in vivo. The result suggests an interaction between the Hippo and TERT signaling pathways. We also propose that SMG6 and TERT are novel molecular target candidates for LATS2-inactivated cancers such as MM.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
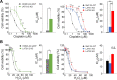



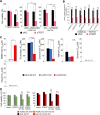
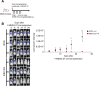
References
-
- Gomez DR, Rimner A, Simone CB, Cho BCJ, de Perrot M, Adjei AA, et al. The use of radiation therapy for the treatment of malignant pleural mesothelioma: expert opinion from the National Cancer Institute Thoracic Malignancy Steering Committee, International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer, and Mesothelioma Applied Research Foundation. J Thorac Oncol. 2019;14:1172–83. - PubMed
-
- Murthy SS, Testa JR. Asbestos, chromosomal deletions, and tumor suppressor gene alterations in human malignant mesothelioma. J Cell Physiol. 1999;180:150–7. - PubMed
-
- Rosenzweig KE, Giraud P. Radiation therapy for malignant pleural mesothelioma. Cancer Radiotherapie. 2017;21:73–76. - PubMed
-
- Baas P, Scherpereel A, Nowak AK, Fujimoto N, Peters S, Tsao AS, et al. First-line nivolumab plus ipilimumab in unresectable malignant pleural mesothelioma (CheckMate 743): a multicentre, randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2021;397:375–86. - PubMed
-
- Bueno R, Stawiski EW, Goldstein LD, Durinck S, de Rienzo A, Modrusan Z, et al. Comprehensive genomic analysis of malignant pleural mesothelioma identifies recurrent mutations, gene fusions and splicing alterations. Nat Genet. 2016;48:407–16. - PubMed
Grants and funding
- JP19ck0106368/Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (AMED)
- JP21K06863/MEXT | Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS)
- JP18K06979/MEXT | Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS)
- JP15K08325/MEXT | Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS)
- JP19K16809/MEXT | Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

