Structural basis for the activation of the lipid scramblase TMEM16F
- PMID: 36335104
- PMCID: PMC9637102
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-34497-x
Structural basis for the activation of the lipid scramblase TMEM16F
Abstract
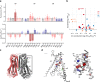
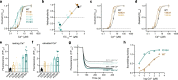
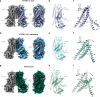
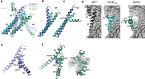
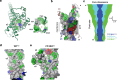
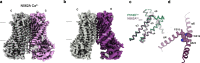
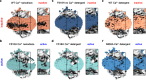
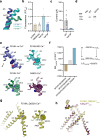
TMEM16F, a member of the conserved TMEM16 family, plays a central role in the initiation of blood coagulation and the fusion of trophoblasts. The protein mediates passive ion and lipid transport in response to an increase in intracellular Ca2+. However, the mechanism of how the protein facilitates both processes has remained elusive. Here we investigate the basis for TMEM16F activation. In a screen of residues lining the proposed site of conduction, we identify mutants with strongly activating phenotype. Structures of these mutants determined herein by cryo-electron microscopy show major rearrangements leading to the exposure of hydrophilic patches to the membrane, whose distortion facilitates lipid diffusion. The concomitant opening of a pore promotes ion conduction in the same protein conformation. Our work has revealed a mechanism that is distinct for this branch of the family and that will aid the development of a specific pharmacology for a promising drug target.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Suzuki J, Umeda M, Sims PJ, Nagata S. Calcium-dependent phospholipid scrambling by TMEM16F. Nature. 2010;468:834–838. - PubMed
-
- Bevers EM, Williamson PL. Getting to the Outer Leaflet: Physiology of Phosphatidylserine Exposure at the Plasma Membrane. Physiol. Rev. 2016;96:605–645. - PubMed
-
- Pedemonte N, Galietta LJ. Structure and function of TMEM16 proteins (anoctamins) Physiol. Rev. 2014;94:419–459. - PubMed
-
- Castoldi E, Collins PW, Williamson PL, Bevers EM. Compound heterozygosity for 2 novel TMEM16F mutations in a patient with Scott syndrome. Blood. 2011;117:4399–4400. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

