Interaction of a viral insulin-like peptide with the IGF-1 receptor produces a natural antagonist
- PMID: 36335114
- PMCID: PMC9637144
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-34391-6
Interaction of a viral insulin-like peptide with the IGF-1 receptor produces a natural antagonist
Abstract
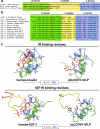
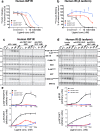
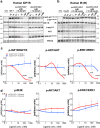
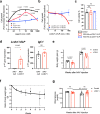
Lymphocystis disease virus-1 (LCDV-1) and several other Iridoviridae encode viral insulin/IGF-1 like peptides (VILPs) with high homology to human insulin and IGFs. Here we show that while single-chain (sc) and double-chain (dc) LCDV1-VILPs have very low affinity for the insulin receptor, scLCDV1-VILP has high affinity for IGF1R where it can antagonize human IGF-1 signaling, without altering insulin signaling. Consequently, scLCDV1-VILP inhibits IGF-1 induced cell proliferation and growth hormone/IGF-1 induced growth of mice in vivo. Cryo-electron microscopy reveals that scLCDV1-VILP engages IGF1R in a unique manner, inducing changes in IGF1R conformation that led to separation, rather than juxtaposition, of the transmembrane segments and hence inactivation of the receptor. Thus, scLCDV1-VILP is a natural peptide with specific antagonist properties on IGF1R signaling and may provide a new tool to guide development of hormonal analogues to treat cancers or metabolic disorders sensitive to IGF-1 without affecting glucose metabolism.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
M.C.L.’s laboratory has a funded agreement with Eli Lilly and Company to conduct research not connected to this publication. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A viral insulin-like peptide inhibits IGF-1 receptor phosphorylation and regulates IGF1R gene expression.Mol Metab. 2024 Feb;80:101863. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2023.101863. Epub 2024 Jan 3. Mol Metab. 2024. PMID: 38182007 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of viral insulins reveals white adipose tissue-specific effects in mice.Mol Metab. 2021 Feb;44:101121. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2020.101121. Epub 2020 Nov 19. Mol Metab. 2021. PMID: 33220491 Free PMC article.
-
A viral insulin-like peptide is a natural competitive antagonist of the human IGF-1 receptor.Mol Metab. 2021 Nov;53:101316. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2021.101316. Epub 2021 Aug 13. Mol Metab. 2021. PMID: 34400347 Free PMC article.
-
Cell cycle control by the insulin-like growth factor signal: at the crossroad between cell growth and mitotic regulation.Cell Cycle. 2023 Jan;22(1):1-37. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2022.2108117. Epub 2022 Aug 25. Cell Cycle. 2023. PMID: 36005738 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Crosstalk between insulin-like growth factor (IGF) receptor and integrins through direct integrin binding to IGF1.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2017 Apr;34:67-72. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2017.01.003. Epub 2017 Feb 3. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2017. PMID: 28190785 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Effects of Viruses on Insulin Sensitivity and Blood-Brain Barrier Function.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 25;24(3):2377. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032377. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36768699 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fish-hunting cone snail disrupts prey's glucose homeostasis with weaponized mimetics of somatostatin and insulin.Nat Commun. 2024 Aug 20;15(1):6408. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-50470-2. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39164229 Free PMC article.
-
vPIF-1 is an insulin-like antiferroptotic viral peptide.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 May 23;120(21):e2300320120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2300320120. Epub 2023 May 15. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023. PMID: 37186845 Free PMC article.
-
EWS/FLI1 Characterization, Activation, Repression, Target Genes and Therapeutic Opportunities in Ewing Sarcoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 14;24(20):15173. doi: 10.3390/ijms242015173. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37894854 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Novel Peptide COX52-69 Inhibits High Glucose-induced Insulin Secretion by Modulating BK Channel Activity.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2024;25(5):419-426. doi: 10.2174/0113892037249620231010063637. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2024. PMID: 37885106
References
-
- Chassin D, Laurent A, Janneau JL, Berger R, Bellet D. Cloning of a new member of the insulin gene superfamily (INSL4) expressed in human placenta. Genomics. 1995;29:465–470. - PubMed
-
- Hsu SY. Cloning of two novel mammalian paralogs of relaxin/insulin family proteins and their expression in testis and kidney. Mol. Endocrinol. 1999;13:2163–2174. - PubMed
-
- Lok S, et al. Identification of INSL6, a new member of the insulin family that is expressed in the testis of the human and rat. Biol. Reprod. 2000;62:1593–1599. - PubMed
-
- Conklin D, et al. Identification of INSL5, a new member of the insulin superfamily. Genomics. 1999;60:50–56. - PubMed
-
- Bathgate RA, et al. Human relaxin gene 3 (H3) and the equivalent mouse relaxin (M3) gene. Novel members of the relaxin peptide family. J. Biol. Chem. 2002;277:1148–1157. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

