Autoinducer-2 and bile salts induce c-di-GMP synthesis to repress the T3SS via a T3SS chaperone
- PMID: 36335118
- PMCID: PMC9637222
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-34607-9
Autoinducer-2 and bile salts induce c-di-GMP synthesis to repress the T3SS via a T3SS chaperone
Abstract
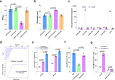
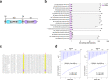
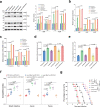
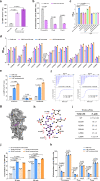
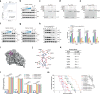
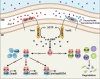
Cyclic di-GMP (c-di-GMP) transduces extracellular stimuli into intracellular responses, coordinating a plethora of important biological processes. Low levels of c-di-GMP are often associated with highly virulent behavior that depends on the type III secretion system (T3SS) effectors encoded, whereas elevated levels of c-di-GMP lead to the repression of T3SSs. However, extracellular signals that modulate c-di-GMP metabolism to control T3SSs and c-di-GMP effectors that relay environmental stimuli to changes in T3SS activity remain largely obscure. Here, we show that the quorum sensing signal autoinducer-2 (AI-2) induces c-di-GMP synthesis via a GAPES1 domain-containing diguanylate cyclase (DGC) YeaJ to repress T3SS-1 gene expression in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. YeaJ homologs capable of sensing AI-2 are present in many other species belonging to Enterobacterales. We also reveal that taurocholate and taurodeoxycholate bind to the sensory domain of the DGC YedQ to induce intracellular accumulation of c-di-GMP, thus repressing the expression of T3SS-1 genes. Further, we find that c-di-GMP negatively controls the function of T3SSs through binding to the widely conserved CesD/SycD/LcrH family of T3SS chaperones. Our results support a model in which bacteria sense changes in population density and host-derived cues to regulate c-di-GMP synthesis, thereby modulating the activity of T3SSs via a c-di-GMP-responsive T3SS chaperone.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

