Pulmonary function in school-age children following intravitreal injection of bevacizumab for retinopathy of prematurity
- PMID: 36335152
- PMCID: PMC9637204
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-22338-2
Pulmonary function in school-age children following intravitreal injection of bevacizumab for retinopathy of prematurity
Abstract
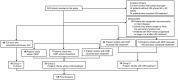
The effect of anti-vascular endothelial growth factor on neonatal lung development was inconclusive. To evaluate pulmonary function in school-age children who have received intravitreal bevacizumab (IVB) for retinopathy of prematurity (ROP), this study included 118 school-aged children who were grouped into three groups: full-term control children (group 1), preterm children who had not received IVB treatment (group 2) and preterm children with ROP who had received IVB treatment (group 3). Pulmonary function was measured by spirometry and impulse oscillometry. Pulmonary function was significantly better in group 1 than in groups 2 and 3 (all p < 0.05 in forced vital capacity (FVC), forced expiratory volume in 1 s (FEV1), forced expiratory flow between 25 and 75% of FVC (FEF25-75), and respiratory resistance at 5 Hz and difference between respiratory resistance at 5 and 20 Hz (R5-R20). There were no statistically significant differences between group 2 and group 3 in all pulmonary function parameters, including FVC, FEV1, ratio of FEV1 to FVC, FEF25-75, R5, R20, R5-R20, and respiratory reactance at 5 Hz. In conclusion, our study revealed that preterm infants receiving IVB for ROP had comparable pulmonary function at school age to their preterm peers who had not received IVB treatment.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Refractive outcome of intravitreal bevacizumab injection in comparison to spontaneous regression of retinopathy of prematurity (ROP).Strabismus. 2020 Mar;28(1):49-54. doi: 10.1080/09273972.2019.1697302. Epub 2019 Dec 2. Strabismus. 2020. PMID: 31790628
-
Intravitreal Bevacizumab Is Associated With Prolonged Ventilatory Support in Preterm Infants With Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia.Chest. 2022 Dec;162(6):1328-1337. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2022.06.017. Epub 2022 Jun 23. Chest. 2022. PMID: 35753385
-
Respiratory outcomes in preterm infants following intravitreal bevacizumab for retinopathy of prematurity-a 10-year matched case study.Eye (Lond). 2023 Dec;37(17):3675-3681. doi: 10.1038/s41433-023-02579-9. Epub 2023 Jul 3. Eye (Lond). 2023. PMID: 37400566 Free PMC article.
-
Neurodevelopmental Outcomes after Bevacizumab Treatment for Retinopathy of Prematurity: A Meta-analysis.Ophthalmology. 2021 Jun;128(6):877-888. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2020.11.012. Epub 2020 Nov 16. Ophthalmology. 2021. PMID: 33212122 Review.
-
Development of refractive error in children treated for retinopathy of prematurity with anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (anti-VEGF) agents: A meta-analysis and systematic review.PLoS One. 2019 Dec 2;14(12):e0225643. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0225643. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31790445 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
[Late sequelae of retinopathy of prematurity in infancy].Ophthalmologie. 2023 Jun;120(6):588-596. doi: 10.1007/s00347-023-01876-8. Epub 2023 May 23. Ophthalmologie. 2023. PMID: 37221277 Review. German.
-
Association between telomere length and atopic dermatitis among school-age children.Clin Transl Allergy. 2025 Jun;15(6):e70066. doi: 10.1002/clt2.70066. Clin Transl Allergy. 2025. PMID: 40437344 Free PMC article.
-
Lung volumes, gas transfer and oscillometry after preterm birth: systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur Respir Rev. 2025 May 28;34(176):240151. doi: 10.1183/16000617.0151-2024. Print 2025 Apr. Eur Respir Rev. 2025. PMID: 40436611 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

