The NLRP3 inflammasome: activation and regulation
- PMID: 36336552
- PMCID: PMC10023278
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tibs.2022.10.002
The NLRP3 inflammasome: activation and regulation
Abstract
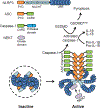
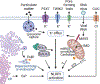
The NOD-, LRR- and pyrin domain-containing protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome is a cytoplasmic supramolecular complex that is activated in response to cellular perturbations triggered by infection and sterile injury. Assembly of the NLRP3 inflammasome leads to activation of caspase-1, which induces the maturation and release of interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and IL-18, as well as cleavage of gasdermin D (GSDMD), which promotes a lytic form of cell death. Production of IL-1β via NLRP3 can contribute to the pathogenesis of inflammatory disease, whereas aberrant IL-1β secretion through inherited NLRP3 mutations causes autoinflammatory disorders. In this review, we discuss recent developments in the structure of the NLRP3 inflammasome, and the cellular processes and signaling events controlling its assembly and activation.
Keywords: Golgi; metabolism; mitochondria; phosphorylation; potassium efflux; ubiquitination.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Mangan MSJ et al. (2018) Targeting the NLRP3 inflammasome in inflammatory diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov 17 (8), 588–606. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

