N-Phenyl- N-[(E)-2-(4,4,5,5-tetra-methyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl)ethen-yl]aniline
- PMID: 36337091
- PMCID: PMC9028550
- DOI: 10.1107/S2414314622000839
N-Phenyl- N-[(E)-2-(4,4,5,5-tetra-methyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl)ethen-yl]aniline
Abstract
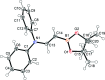
The title compound, C20H24BNO2, has a polarized π-system due to significant resonance between the N-C(H)=C(H)-B and ionic N+=C(H)-C(H)=B- canonical forms. The dihedral angles between the NC2B plane (r.m.s. deviation 0.0223 Å) and the C3N (r.m.s. deviation 0.0025 Å) and BCO2 (r.m.s. deviation 0.0044 Å) planes are 2.51 (12) and 3.09 (19)°, respectively. This indicates the lone pair of the nitro-gen atom and a vacant p orbital of the boron atom are conjugated with the central C=C bond. In comparison with the carbazole analogue [Hatayama & Okuno (2012 ▸). Acta Cryst. E68, o84], the C-N and C-B bonds are shorter. The results are well explained by the increase in the contribution of the N+=C(H)-C(H)=B- canonical form in the title compound.
Keywords: crystal structure; dioxaborolan-2-yl; resonance.
© Hatayama et al. 2022.
Figures
References
-
- Farrugia, L. J. (2012). J. Appl. Cryst. 45, 849–854.
-
- Onuma, K., Suzuki, K. & Yamashita, M. (2015). Chem. Lett. 44, 405–407.
-
- Rigaku (1999). NUMABS. Rigaku Corporation, Tokyo, Japan.
-
- Rigaku (2008). CrystalClear. Rigaku Corporation, Tokyo, Japan.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous