Di-ammonium potassium citrate, (NH4)2KC6H5O7
- PMID: 36337153
- PMCID: PMC9462224
- DOI: 10.1107/S2414314620006124
Di-ammonium potassium citrate, (NH4)2KC6H5O7
Abstract
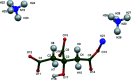
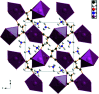
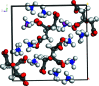
The crystal structure of di-ammonium potassium citrate, 2NH4 +·K+·C6H5O7 3-, has been solved and refined using laboratory X-ray powder diffraction data and optimized using density functional theory. The KO7 coordination polyhedra are isolated. The ammonium cations and the hydro-phobic methyl-ene sides of the citrate anions occupy the spaces between the coordination polyhedra. Each hydrogen atom of the ammonium ions acts as a donor in a charge-assisted N-H⋯O, N-H⋯(O,O) or N-H⋯(O,O,O) hydrogen bond. There is an intra-molecular O-H⋯O hydrogen bond in the citrate anion between the hydroxide group and one of the terminal carboxyl-ate groups.
Keywords: ammonium; citrate anion; density functional theory; potasssium; powder diffraction.
© Patel et al. 2020.
Figures


References
-
- Altomare, A., Cuocci, C., Giacovazzo, C., Moliterni, A., Rizzi, R., Corriero, N. & Falcicchio, A. (2013). J. Appl. Cryst. 46, 1231–1235.
-
- Bravais, A. (1866). Etudes Cristallographiques. Paris: Gauthier Villars.
-
- Bruker (2015). Data Collector. Bruker AXS Inc., Maddison, Wisconsin, USA.
-
- Bruno, I. J., Cole, J. C., Kessler, M., Luo, J., Motherwell, W. D. S., Purkis, L. H., Smith, B. R., Taylor, R., Cooper, R. I., Harris, S. E. & Orpen, A. G. (2004). J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 44, 2133–2144. - PubMed
-
- Crystal Impact (2015). DIAMOND. Crystal Impact GbR, Bonn, Germany.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
