Poly[bis-[μ2-4,4'-bis-(imidazol-1-ylmeth-yl)biphenyl-κ2 N: N']di-chlorido-nickel(II)]
- PMID: 36337687
- PMCID: PMC9462028
- DOI: 10.1107/S2414314622003777
Poly[bis-[μ2-4,4'-bis-(imidazol-1-ylmeth-yl)biphenyl-κ2 N: N']di-chlorido-nickel(II)]
Abstract
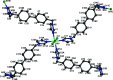
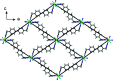
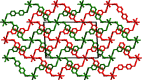
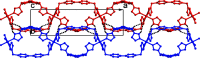
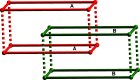
In the title compound, [NiCl2(C20H18N4)2] n , the Ni2+ cation is situated on an inversion center and is coordinated by two chloride ions and four imidazole N atoms of four different 4,4'-bis-[(1H-imidazol-1-yl)meth-yl]-1,1'-biphenyl (BIMB), forming a slightly distorted octa-hedral geometry. Each BIMB ligand adopts a linear linker to connect Ni2+ ions, forming a two-dimensional layer with an sql network. In the crystal, neighboring layers repeat in an ABAB stacking mode, and weak inter-molecular C-H⋯Cl hydrogen bonds between alternate layers lead to a three-dimensional, twofold inter-penetrated, supra-molecular framework with a pcu topology net.
Keywords: coordination polymer; crystal structure; imidazole; nickel.
© Deng et al. 2022.
Figures










References
-
- Banerjee, R., Phan, A., Wang, B., Knobler, C., Furukawa, H., O’Keeffe, M. & Yaghi, O. M. (2008). Science, 319, 939–943. - PubMed
-
- Brandenburg, K. (1999). DIAMOND. Crystal Impact GbR, Bonn, Germany.
-
- Chen, B., Yang, Z., Zhu, Y. & Xia, Y. (2014). J. Mater. Chem. A, 2, 16811–16831.
-
- Rigaku OD (2015). CrysAlis PRO. Rigaku Oxford Diffraction, Yarnton, England.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
