Di-chlorido-bis-[2-(pyridin-2-yl-κ N)-1 H-benzimidazole-κ N 3]nickel(II) monohydrate
- PMID: 36337723
- PMCID: PMC9462142
- DOI: 10.1107/S2414314620000401
Di-chlorido-bis-[2-(pyridin-2-yl-κ N)-1 H-benzimidazole-κ N 3]nickel(II) monohydrate
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Di-chlorido-bis-[2-(pyridin-2-yl-κN)-1H-benzimidazole-κN 3]nickel(II) monohydrate. Corrigendum.IUCrdata. 2020 May 29;5(Pt 5):x200688. doi: 10.1107/S2414314620006884. eCollection 2020 May. IUCrdata. 2020. PMID: 36342901 Free PMC article.
Abstract
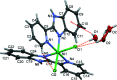
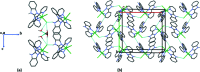
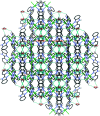
In the title complex, [NiCl2(C12H9N3)2]·H2O, a divalent nickel atom is coordinated by two 2-(pyridin-2-yl)-1H-benzimidazole ligands in a slightly distorted octa-hedral environment defined by four N donors of two N,N'-chelating ligands, along with two cis-oriented anionic chloride donors. The title complex crystallized with a water mol-ecule disordered over two positions. In the crystal, a combination of O-H⋯Cl, O-H.·O and N-H⋯Cl hydrogen bonds, together with C-H⋯O, C-H⋯Cl and C-H⋯π inter-actions, links the complex mol-ecules and the water mol-ecules to form a supra-molecular three-dimensional framework. The title complex is isostructural with the cobalt(II) dichloride complex reported previously [Das et al. (2011 ▸). Org. Biomol. Chem. 9, 7097-7107].
Keywords: 2-(pyridin-2-yl)-1H-benzimidazole; C—H⋯π interactions; crystal structure; hydrogen bonding; nickel(II) complex; transfer hydrogenation.
© MacNeil et al. 2020.
Figures

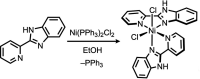
References
-
- Abubakar, S. & Bala, M. D. (2018). J. Coord. Chem. 71, 2913–2923.
-
- Chen, Z., Zeng, M., Zhang, Y., Zhang, Z. & Liang, F. (2010). Appl. Organomet. Chem. 24, 625–630.
-
- Das, S., Guha, S., Banerjee, A., Lohar, S., Sahana, A. & Das, D. (2011). Org. Biomol. Chem. 9, 7097–7104. - PubMed
-
- Dolomanov, O. V., Bourhis, L. J., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A. K. & Puschmann, H. (2009). J. Appl. Cryst. 42, 339–341.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
