Effects of amikacin, polymyxin-B, and sulbactam combination on the pharmacodynamic indices of mutant selection against multi-drug resistant Acinetobacter baumannii
- PMID: 36338049
- PMCID: PMC9632654
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1013939
Effects of amikacin, polymyxin-B, and sulbactam combination on the pharmacodynamic indices of mutant selection against multi-drug resistant Acinetobacter baumannii
Abstract
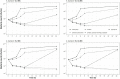
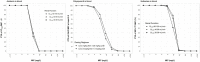
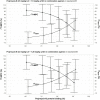
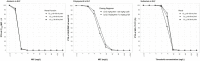
Amikacin and polymyxins as monotherapies are ineffective against multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii at the clinical dose. When polymyxins, aminoglycosides, and sulbactam are co-administered, the combinations exhibit in vitro synergistic activities. The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) and mutant prevention concentration (MPC) were determined in 11 and 5 clinical resistant isolates of A. baumannii harboring OXA-23, respectively, in order to derive the fraction of time over the 24-h wherein the free drug concentration was within the mutant selection window (fTMSW) and the fraction of time that the free drug concentration was above the MPC (fT>MPC) from simulated pharmacokinetic profiles. The combination of these three antibiotics can confer susceptibility in multi-drug resistant A. baumannii and reduce the opportunity for bacteria to develop further resistance. Clinical intravenous dosing regimens of amikacin, polymyxin-B, and sulbactam were predicted to optimize fTMSW and fT>MPC from drug exposures in the blood. Mean fT>MPC were ≥ 60% and ≥ 80% for amikacin and polymyxin-B, whereas mean fTMSW was reduced to <30% and <15%, respectively, in the triple antibiotic combination. Due to the low free drug concentration of amikacin and polymyxin-B simulated in the epithelial lining fluid, the two predicted pharmacodynamic parameters in the lung after intravenous administration were not optimal even in the combination therapy setting.
Keywords: Acinetobacter baumannii; OXA-23; amikacin; pharmacodynamics; polymyxin-B; sulbactam.
Copyright © 2022 Zhu, Song, Zhang, Diao, Heinrichs, Martins, Lv, Zhu, Yu and Sy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Al Atrouni A., Hamze M., Jisr T., Lemarie C., Eveillard M., Joly-Guillou M. L., et al. . (2016). Wide spread of OXA-23-producing carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii belonging to clonal complex II in different hospitals in Lebanon. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 52, 29–36. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2016.09.017, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
-
- Aydemir H., Akduman D., Piskin N., Comert F., Horuz E., Terzi A., et al. . (2013). Colistin vs. the combination of colistin and rifampicin for the treatment of carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii ventilator-associated pneumonia. Epidemiol. Infect. 141, 1214–1222. doi: 10.1017/S095026881200194X, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

