ERCC1 is a potential biomarker for predicting prognosis, immunotherapy, chemotherapy efficacy, and expression validation in HER2 over-expressing breast cancer
- PMID: 36338712
- PMCID: PMC9631216
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.955719
ERCC1 is a potential biomarker for predicting prognosis, immunotherapy, chemotherapy efficacy, and expression validation in HER2 over-expressing breast cancer
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the relationship between Excision repair cross-complementation 1 (ERCC1) expression, clinicopathological features, and breast cancer prognosis in patients treated with trastuzumab. Further, we aim to explore the immune status of ERCC1 in breast cancer.
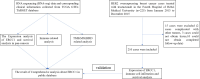
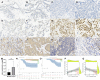
Methods: The data were retrieved from publicly available databases like the Cancer Genome Atlas, Therapeutically Applicable Research to Generate Effective Treatments, and the Genotype-Tissue Expression. The data was used to perform differential expression analyses between tumor and normal tissues in pan-cancers, immune-related analysis, homologous recombination deficiency (HRD), tumor mutation burden, and microsatellite instability. A total of 210 patients with HER2 over-expressing breast cancer from the Fourth Hospital of Hebei Medical University between January 2013 to December 2015 were enrolled in the study. Ten adjacent normal tissues were used to study the expression pattern of ERCC1 in normal tissues. Immunohistochemistry was performed to study ERCC1 expression and immune cell infiltration in different status of ERCC1 expression. Further, the correlation between ERCC1 expression, immune cell infiltration clinicopathological features, and the prognosis of patients with breast cancer was analyzed.
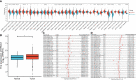
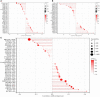
Results: The immune analysis revealed a significant correlation between CD8+ T cell, CD4+ T cell, T helper cell, macrophages, mast cells, and ERCC1 expression. Spearman analysis show that ERCC1 expression is related to macrophages and T cells. A close correlation was observed between increased ERCC1 expression and high tumor immune dysfunction and exclusion (TIDE) score as well as HRD. The results revealed a significant correlation among ERCC1, chemotherapy and estrogen receptor (ER; P < 0.05) expression. Univariate survival analysis revealed a significant correlation (P < 0.05) between that ERCC1 and ER expression, blood vessel invasion, and disease-free survival (DFS). ERCC1 and ER expression, tumor size, blood vessel invasion, pathological type, and lymph node metastases significantly correlated (P < 0.05) with overall survival in patients. Multivariate regression analysis revealed that ERCC1 expression and chemotherapy were independent factors that influence DFS. ERCC1 expression and vascular tumor thrombus were independent influencing factors that influence OS.
Conclusion: A correlation was observed between high ERCC1 expression and poor patient prognosis. High ERCC1 expression also influences the efficacy of immunotherapy and chemotherapy.
Keywords: breast cancer; clinicopathological feature; excision repair cross-complementary gene 1; human epidermal growth factor receptor-2; prognosis.
Copyright © 2022 Li, Liao and Ma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

