Tris(1 H-benzimidazol-2-ylmeth-yl)amine methanol tris-olvate
- PMID: 36339476
- PMCID: PMC9462197
- DOI: 10.1107/S2414314620002813
Tris(1 H-benzimidazol-2-ylmeth-yl)amine methanol tris-olvate
Abstract
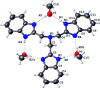
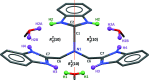
The structure of the tertiary amine tris-(1H-benzimidazol-2-ylmeth-yl)amine (C24H21N7, abbreviated ntb) has been previously reported twice as solvates, namely the monohydrate and the aceto-nitrile-methanol-water (1/0.5/1.5) solvate, both with the tripodal conformation formed via multiple hydrogen bonds. Now, we report the tri-methanol adduct, ntb·3CH3OH, where the amine has the stair conformation featuring one benzimidazole group oriented in the opposite direction from the other two. The asymmetric unit contains one-half amine, completed through the mirror plane m in space group Pmn21 to form the ntb mol-ecule, with the H atom for each imidazole moiety equally disordered between both N sites available in the imidazole ring. The asymmetric unit also contains one and a half methanol mol-ecules, one being placed in general position with the hy-droxy H atom disordered over two sites with occupancy ratio 1:1, while the other lies on the m mirror plane, and has thus its hy-droxy H atom disordered by symmetry. As in the previously reported solvates, all imine and amine groups of the ntb mol-ecules and the methanol mol-ecules are involved in N-H⋯O and O-H⋯N hydrogen bonds. In the title compound, however, the involved H atom is systematically a disordered H atom provided by an imidazole group or a methanol mol-ecule.
Keywords: crystal structure; hydrogen bonds; methanol solvate; molecular conformation; tripodal N-donor ligand.
© Anzaldo-Olivares et al. 2020.
Figures
References
-
- Agilent (2012). CrysAlis PRO and CrysAlis RED. Agilent Technologies, Yarnton, England.
-
- Dolomanov, O. V., Bourhis, L. J., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A. K. & Puschmann, H. (2009). J. Appl. Cryst. 42, 339–341.
-
- Kwak, B., Woong Cho, K., Pyo, M. & Soo Lah, M. (1999). Inorg. Chim. Acta, 290, 21–27.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
