Systematic review of Lonicerae Japonicae Flos: A significant food and traditional Chinese medicine
- PMID: 36339557
- PMCID: PMC9626961
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1013992
Systematic review of Lonicerae Japonicae Flos: A significant food and traditional Chinese medicine
Abstract
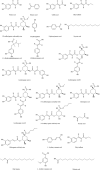
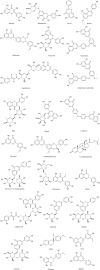
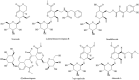
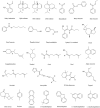
Lonicerae Japonicae Flos has been used as a tea and medicine for more than 1,500 years. It has the functions of clearing heat, detoxification, and is often used to treat carbuncle, furuncle, throat arthralgia, erysipelas, heat-toxic blood dysentery, febrile fever. This paper summarizes the botany, ethnopharmacology, chemical composition and pharmacological action of Lonicerae Japonicae Flos from 1986 to 2022, and looks forward to the future research direction of Lonicerae Japonicae Flos. At present, the components isolated from Lonicerae Japonicae Flos include essential oils, organic acids, flavonoids, iridoids, saponins and other compounds. It has the effects of anti-inflammation, anti-virus, anti-bacteria, anti-oxidation, anti-tumor, protect liver and galltesticles, hypotensive, hypolipidemic, anti-thrombosis, anti-allergy, immune regulation and so on. It is often used in clinical treatment of diarrhea, hematochezia, febrile disease, exogenous wind-heat, and cold, swelling and toxin of carbuncle, sore throat and so on. The comprehensive evaluation of the quality of Lonicerae Japonicae Flos and the understanding of multi-target network pharmacology also need to be studied. As a kind of health food with high value, LJF is worthy of further promotion and development.
Keywords: Lonicerae Japonicae Flos; botany; ethnopharmacology; pharmacology; phytochemistry; toxicology.
Copyright © 2022 Zheng, Liu, Hou, Wang, Na, Hu, Jiang and Yang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Bai X., Chai Y., Shi W., Li Y., Zhang T., Liu P. (2020). Lonicera japonica polysaccharides attenuate ovalbumin-induced allergic rhinitis by regulation of Th17 cells in BALB/c mice. J. Funct. Foods 65, 103758. 10.1016/j.jff.2019.103758 - DOI
-
- Chen J. J., Fang J., Wan J., Feng L., Zhang Y., Zhao J. H., et al. (2009). An in vitro study of the anti-cytomegalovirus effect of chlorogenic acid. Her. Med. 28 (9), 1138–1141.
-
- Chen L., Zhang H. Y., Li X., Dong J. J., Zhao T. Z. (2015). Research progress on chemical constituents of Lonicera japonica . Drugs Clin. 30 (1), 108–114.
-
- Chen X. L. (2010). Effects of water extract from lonicerae japonicae flos on glycometabolism in vitro . Lishizhen Med. Mat. Med. Res. 21 (3), 628–629. 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0805.2010.03.056 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

