(E)-5-(4-Methyl-benzyl-idene)-1-phenyl-4,5,6,7-tetra-hydro-1 H-indazol-4-one
- PMID: 36339806
- PMCID: PMC9462011
- DOI: 10.1107/S2414314622002838
(E)-5-(4-Methyl-benzyl-idene)-1-phenyl-4,5,6,7-tetra-hydro-1 H-indazol-4-one
Abstract
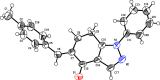
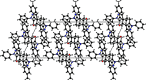
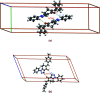
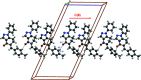
In the title compound, C21H18N2O, the non-aromatic six-membered ring adopts a distorted envelope conformation with one of the methyl-ene-C atoms being the flap atom. The dihedral angle between the phenyl and 4-tolyl rings is 75.3 (1)°. The 1,2-diazole ring forms dihedral angles of 41.9 (1) and 65.5 (1)° with the phenyl and 4-tolyl rings, respectively. In the crystal, stabilizing C-H⋯O, C-H⋯π and π-π inter-actions are evident. The calculated Hirshfeld surfaces highlight the prominent role of C-H⋯O inter-actions (8.6%), along with H⋯H (51.7%) and C⋯H/H⋯C (29.2%) surface contacts.
Keywords: Hirshfeld surface; crystal structure; indazol-4-one.
© Meenatchi et al. 2022.
Figures



References
-
- Bernstein, J., Davis, R. E., Shimoni, L. & Chang, N. L. (1995). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 34, 1555–1573.
-
- Bruker (2009). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
-
- Faisal, M., Saeed, A., Hussain, S., Dar, P. & Larik, F. A. (2019). J. Chem. Sci. 131, article No. 70. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12039-019-1646-1
-
- Farrugia, L. J. (2012). J. Appl. Cryst. 45, 849–854.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
