Acute interstitial nephritis manifesting as a persistent nephogram
- PMID: 36340231
- PMCID: PMC9633567
- DOI: 10.1016/j.radcr.2022.10.010
Acute interstitial nephritis manifesting as a persistent nephogram
Abstract
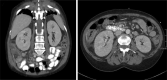
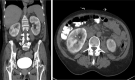
We report a case of a 61-year-old woman who presented to the emergency department with high inflammatory parameters and acute renal failure. Marked enlarged kidneys with persistent nephrogram were found on contrast-enhanced computed tomography . Renal biopsy showed acute interstitial nephritis. Acute interstitial nephritis must be included in the differential diagnosis in patients presenting with a persistent nephrogram.
Keywords: Acute interstitial nephritis; Contrast-enhanced computed tomography; Kidney biopsy; Persistent nephrogram.
© 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. on behalf of University of Washington.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Infliximab-Induced Tubulointerstitial Nephritis with Image Findings of Striated Nephrogram in Crohn's Disease.Tohoku J Exp Med. 2018 Jul;245(3):149-152. doi: 10.1620/tjem.245.149. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2018. PMID: 29973427
-
Allergic Interstitial Nephritis Manifesting as a Striated Nephrogram.Case Rep Med. 2015;2015:250530. doi: 10.1155/2015/250530. Epub 2015 Nov 18. Case Rep Med. 2015. PMID: 26664405 Free PMC article.
-
Positron emission tomography as an adjuvant diagnostic test in the evaluation of checkpoint inhibitor-associated acute interstitial nephritis.J Immunother Cancer. 2019 Dec 21;7(1):356. doi: 10.1186/s40425-019-0820-9. J Immunother Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31864416 Free PMC article.
-
Acute post streptococcal interstitial nephritis in an adult and review of the literature.Int Urol Nephrol. 1999;31(2):145-8. doi: 10.1023/a:1007112422091. Int Urol Nephrol. 1999. PMID: 10481957 Review.
-
[A case of acute interstitial nephritis and nonoliguria acute renal failure induced by cimetidine].Nihon Jinzo Gakkai Shi. 1992 Nov;34(11):1227-32. Nihon Jinzo Gakkai Shi. 1992. PMID: 1294777 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Clinical Implications of Striated Nephrogram in Patients Receiving Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors for Cancer.Kidney Med. 2025 May 29;7(8):101038. doi: 10.1016/j.xkme.2025.101038. eCollection 2025 Aug. Kidney Med. 2025. PMID: 40740732 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Kodner CM, Kudrimoti A. Diagnosis and management of acute interstitial nephritis. Am Fam Physician. 2003;67(12):2527–2534. - PubMed
-
- Naik RH, Annamaraju P. StatPearls [Internet] StatPearls Publishing; Treasure Island, FL: 2022. Interstitial nephritis.
-
- Bhandari J, Thada PK, Arif H. StatPearls [Internet] StatPearls Publishing; Treasure Island, FL: 2022. Tubulointerstitial nephritis. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

