Prognostic Impact of Echocardiographic Congestion Grade in HFpEF With and Without Atrial Fibrillation
- PMID: 36340256
- PMCID: PMC9627800
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jacasi.2021.10.012
Prognostic Impact of Echocardiographic Congestion Grade in HFpEF With and Without Atrial Fibrillation
Abstract
Background: Atrial fibrillation (AF) is common in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF).
Objectives: This study aimed to investigate the prognostic value of echocardiographic markers of congestion that can be applied to both AF and patients without AF with HFpEF.
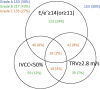
Methods: We conducted a multicenter study of 505 patients with HFpEF admitted to hospitals for acute decompensated heart failure. The ratio of early diastolic transmitral flow velocity to mitral annulus velocity (E/e'), the tricuspid regurgitation peak velocity, and the collapsibility of the inferior vena cava were obtained at discharge. Congestion was determined by echocardiography if any one of E/e' ≥14 (E/e' ≥11 for AF), tricuspid regurgitation peak velocity ≥2.8 m/s, or inferior vena cava collapsibility <50% was positive. We classified patients into grade A, grade B, and grade C according to the number of positive congestion indices. The primary endpoint was the composite of cardiovascular death and heart failure hospitalization.
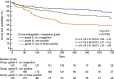
Results: During the follow-up period (median: 373 days), 162 (32%) patients experienced the primary endpoint. Grade C patients had a higher risk for the primary endpoint than grade A (HR: 2.98; 95% CI: 1.97-4.52) and grade B patients (HR: 1.92; 95% CI: 1.29-2.86) (log-rank P < 0.0001). Echocardiographic congestion grade improved the predictive value when added to the age, sex, New York Heart Association functional class, and N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide, not only in sinus rhythm (Uno C-statistic: 0.670 vs 0.655) but in AF (Uno C-statistic: 0.667 vs 0.639).
Conclusions: Echocardiographic congestion grade has prognostic value in patients with HFpEF with and without AF.
Keywords: AF, atrial fibrillation; ASE, American Society of Echocardiography; E/e′, ratio of early diastolic transmitral flow velocity to mitral annulus velocity; EACVI, European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging; HFpEF, heart failure with preserved ejection fraction; IVC, inferior vena cava; IVCC, inferior vena cava collapsibility; NT-proBNP, N-terminal pro–B-type natriuretic peptide; NYHA, New York Heart Association; TRV, tricuspid regurgitation peak velocity; congestion; echocardiography; heart failure with preserved ejection fraction; prognosis.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
This work was funded by Roche Diagnostics K.K. and Fuji Film Toyama Chemical Co. Ltd. Dr Abe has received grants from Boehringer Ingelheim Japan. Dr Hikoso has received personal fees from Daiichi Sankyo Company, Bayer, Astellas Pharma, Pfizer Pharmaceuticals, and Boehringer Ingelheim Japan and has received grants from Roche Diagnostics, Fujifilm Toyama Chemical, and Actelion Pharmaceuticals. Dr Nakatani has received honoraria from Roche Diagnostics. Dr Koretsune has received personal fees from Daiichi Sankyo Company. Dr Sakata has received personal fees from Otsuka Pharmaceutical, Ono Pharmaceutical, Daiichi Sankyo Company, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation, and Actelion Pharmaceuticals and has received grants from Roche Diagnostic, Fujifilm Toyama Chemical, Abbott Medical Japan, Otsuka Pharmaceutical, Daiichi Sankyo Company, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation, and Biotronik. All other authors have reported that they have no relationships relevant to the contents of this paper to disclose.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Prognostic significance of diastolic dysfunction in patients with systolic dysfunction undergoing atrial fibrillation ablation.Int J Cardiol Heart Vasc. 2022 Jul 4;41:101079. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcha.2022.101079. eCollection 2022 Aug. Int J Cardiol Heart Vasc. 2022. PMID: 35812132 Free PMC article.
-
Echocardiographic Evaluation of Left Ventricular Filling Pressure in Patients With Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction: Usefulness of Inferior Vena Cava Measurements and 2016 EACVI/ASE Recommendations.J Card Fail. 2020 Jun;26(6):507-514. doi: 10.1016/j.cardfail.2020.01.018. Epub 2020 Jan 30. J Card Fail. 2020. PMID: 32007555
-
Correlation with invasive left ventricular filling pressures and prognostic relevance of the echocardiographic diastolic parameters used in the 2016 ESC heart failure guidelines and in the 2016 ASE/EACVI recommendations: a systematic review in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction.Eur J Heart Fail. 2018 Sep;20(9):1303-1311. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.1220. Epub 2018 Jun 7. Eur J Heart Fail. 2018. PMID: 29877602
-
Association of Diastolic Dysfunction with N-terminal Pro-B-type Natriuretic Peptide Level in Heart Failure Patients with Preserved Ejection Fraction.Mymensingh Med J. 2019 Apr;28(2):333-346. Mymensingh Med J. 2019. PMID: 31086148
-
Multi-modality assessment of congestion in acute heart failure: Associations with left ventricular ejection fraction and prognosis.Curr Probl Cardiol. 2024 Mar;49(3):102374. doi: 10.1016/j.cpcardiol.2024.102374. Epub 2024 Jan 5. Curr Probl Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 38185433 Review.
Cited by
-
Pulmonary Artery Systolic Pressure and Cava Vein Status in Acute Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction: Clinical and Prognostic Implications.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Feb 12;13(4):692. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13040692. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36832179 Free PMC article.
-
Use of anticoagulation reversal therapy in the emergency department: a single-center real-life retrospective study.World J Emerg Med. 2023;14(1):56-58. doi: 10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2023.004. World J Emerg Med. 2023. PMID: 36713347 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Clinical and Imaging Parameters Associated With Impaired Kidney Function in Patients With Acute Decompensated Heart Failure With Reduced Ejection Fraction.J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2023 Oct;31(4):169-177. doi: 10.4250/jcvi.2023.0004. J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2023. PMID: 37901994 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of Decongestion Status Before Discharge in Acute Decompensated Heart Failure: A Review of Clinical, Biochemical, and Imaging Tools and Their Impact on Management Decisions.Medicina (Kaunas). 2025 Apr 28;61(5):816. doi: 10.3390/medicina61050816. Medicina (Kaunas). 2025. PMID: 40428774 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sex Differences in the Expression of Cardiac Remodeling and Inflammatory Cytokines in Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Atrial Fibrillation.Biomedicines. 2024 May 23;12(6):1160. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12061160. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38927368 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Owan T.E., Hodge D.O., Herges R.M., Jacobsen S.J., Roger V.L., Redfield M.M. Trends in prevalence and outcome of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:251–259. - PubMed
-
- Bozkurt B., Coats A.J.S., Tsutsui H., et al. Universal definition and classification of heart failure: a report of the Heart Failure Society of America, Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology, Japanese Heart Failure Society and Writing Committee of the Universal Definition of Heart Failure: Endorsed by the Canadian Heart Failure Society, Heart Failure Association of India, Cardiac Society of Australia and New Zealand, and Chinese Heart Failure Association. Eur J Heart Fail. 2021;23:352–380. - PubMed
-
- Drazner M.H., Rame J.E., Stevenson L.W., Dries D.L. Prognostic importance of elevated jugular venous pressure and a third heart sound in patients with heart failure. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:574–581. - PubMed
-
- Pellicori P., Graubelli V., Zhang J., et al. IVC diameter in patients with chronic heart failure: relationship and prognostic significance. J Am Coll Cardiol Img. 2013;6:16–28. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

