Management of Alcohol Use Disorder in Patients With Alcoholic Liver Disease
- PMID: 36340303
- PMCID: PMC9630026
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jceh.2022.04.010
Management of Alcohol Use Disorder in Patients With Alcoholic Liver Disease
Abstract
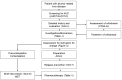
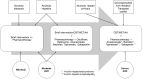
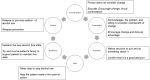
Alcohol use disorder (AUD) is a common condition that develops on the background of heavy alcohol use and is characterised by the loss of control over alcohol use and a compulsion to use alcohol, often despite negative consequences. AUD is a leading cause for the resumption of alcohol use in patients with alcoholic liver disease (ALD) after treatment. Hence it is essential to screen all patients with ALD for the presence of AUD. Screening tools such as alcohol use disorders identification test (AUDIT) and AUDIT-C are used, following which the diagnosis and severity of AUD are determined using DSM-5 criteria. The management of AUD in patients with ALD is best carried out using an integrated approach involving psychiatrists and gastroenterologists/hepatologists. The treatment most often involves a combination of pharmacotherapy and psychosocial interventions which try to achieve and maintain abstinence. Although, there is limited evidence, Baclofen is the first line pharmacological agent for long-term management of AUD in patients with ALD. Intensive psychological interventions such as motivation enhancement therapy and cognitive behavioural therapy are also seen to be beneficial. Treatment retention and follow-up are vital and can positively influence outcomes.
Keywords: AA, Alcoholics Anonymous; ALD, Alcoholic Liver Disease; AMPA, α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid; AUD, Alcohol Use Disorder; AUDIT – C, Alcohol Use Disorder Identification Test – Consumption; AUDIT, Alcohol Use Disorder Identification Test; CBT, Cognitive Behavioural Therapy; CDT, Carbohydrate Deficient Transferrin; CIWA – Ar, Clinical Institute Withdrawal Assessment for Alcohol Revised; DALY, Disability Adjusted Life Years; EtG, Ethyl glucuronide; EtS, Ethyl Sulphate; FAEE, Fatty acid ethyl ester; FDA, Food and Drug Administration; GABA, Gamma-Aminobutyric acid; GGT, Gamma glutamyl transferase; HCV, Hepatitis C Virus; HE, Hepatic Encephalopathy; LT, Liver Transplantation; MCV, Mean corpuscular volume; MET, Motivation Enhancement Therapy; MI, Motivational Interviewing; NMDA, N-Methyl-d-aspartate; PEth, Phosphatidylethanol; RCT, Randomised control trial; SMS, Short Message Service; alcohol use disorder; alcoholic liver disease; diagnosis; pharmacotherapy; psychotherapy.
© 2022 Indian National Association for Study of the Liver. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Management of Alcohol Withdrawal Syndrome in Patients with Alcoholic Liver Disease.J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2022 Nov-Dec;12(6):1527-1534. doi: 10.1016/j.jceh.2022.03.003. Epub 2022 Mar 18. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2022. PMID: 36340306 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New Australian guidelines for the treatment of alcohol problems: an overview of recommendations.Med J Aust. 2021 Oct 4;215 Suppl 7:S3-S32. doi: 10.5694/mja2.51254. Med J Aust. 2021. PMID: 34601742
-
The usefulness of direct ethanol metabolites in assessing alcohol intake in nonintoxicated male patients in an emergency room setting.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2008 Jul;32(7):1284-91. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2008.00696.x. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2008. PMID: 18540912
-
Spectrum, Screening, and Diagnosis of Alcohol-related Liver Disease.J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2023 Jan-Feb;13(1):75-87. doi: 10.1016/j.jceh.2022.10.002. Epub 2022 Oct 13. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2023. PMID: 36647416 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alcoholics Anonymous and other 12-step programs for alcohol use disorder.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Mar 11;3(3):CD012880. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012880.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 32159228 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The Pattern of Alcohol Use in Alcohol-Related Cirrhosis in Indian Patients: AUDIT Indian Liver Study.J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2023 May-Jun;13(3):437-446. doi: 10.1016/j.jceh.2022.12.009. Epub 2022 Dec 24. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2023. PMID: 37250882 Free PMC article.
-
Psychosocial Assessment and Management-related Issues Among Liver Transplant Recipients.J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2024 Jan-Feb;14(1):101261. doi: 10.1016/j.jceh.2023.07.414. Epub 2023 Jul 28. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2024. PMID: 38076366 Free PMC article.
-
Testing a Digital Health App for Patients With Alcohol-Associated Liver Disease: Mixed Methods Usability Study.JMIR Form Res. 2023 Nov 15;7:e47404. doi: 10.2196/47404. JMIR Form Res. 2023. PMID: 37966869 Free PMC article.
-
Optimal Dose of Baclofen for the Treatment of Alcohol Use Disorder: A Systematic Review and Dose-Response Meta-analysis.CNS Drugs. 2025 Jul;39(7):651-667. doi: 10.1007/s40263-025-01188-2. Epub 2025 May 10. CNS Drugs. 2025. PMID: 40347309
-
The Role of Patient-Reported Outcomes in Cirrhosis.Am J Gastroenterol. 2025 May 20;120(8):1708-1719. doi: 10.14309/ajg.0000000000003551. Am J Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 40392245 Review.
References
-
- Hammer J.H., Parent M.C., Spiker D.A., World Health Organization . vol. 65. 2018. (Global Status Report on Alcohol and Health 2018). - DOI
-
- Rehm J. Alcohol Research & Health: Preventing Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism—An Update. [n.d].
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

