Infections and hospital bed-days among aging adults: A five-year retrospective study in a Belgian general hospital
- PMID: 36340588
- PMCID: PMC9632861
- DOI: 10.3389/fmedt.2022.912469
Infections and hospital bed-days among aging adults: A five-year retrospective study in a Belgian general hospital
Abstract
Background: Infectious disease in aging adults (≥61 years) often occurs in combination with other health conditions leading to long hospital stays. Detailed studies on infection in aging adults investigating this problem are sparse.
Aim: To quantify the effect of primary and secondary diagnosed infections on hospitalization bed-days among aging adult patients.
Design: Retrospective patient-file study.
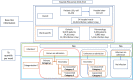
Setting: Ziekenhuis Netwerk Antwerpen (ZNA) Hospital, a 1,858-bed general hospital in Belgium, with 364 beds allocated to geriatric patients.
Data source: Database of hospitalized adult patients aged ≥61 years.
Methods: All adult patients aged ≥61 years hospitalized on two wards, Geriatrics and Pulmonology, from 2010 to 2014 were included. Primary diagnosed infections were defined as infections known at entry to be treated first. Secondary diagnosed infections included infections known at entry but treated in parallel to primary non-infectious causes of entry, infections unknown at entry, and hospital-acquired (nosocomial) infections. Data were analyzed by patient age, gender, year, ward type, bed-days of hospitalization, infection rates, and seasonality.
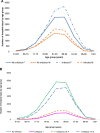
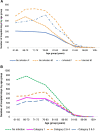
Results: There were 3,306 primary diagnosed infections (18%) and 14,758 secondary infections (82%) identified in the two wards combined (54.7% of all hospital stays at those 2 wards). Secondary diagnosed infections accounted for a significantly higher proportion of hospitalizations in both wards (+40% for Geriatric ward; +20% for Pulmonology ward; p < 0.001) and were associated with a significantly longer average hospital stay (+4 days for Geriatric ward; +5 days for Pulmonology ward; p < 0.001). Nosocomial infections (12% for Geriatric ward; 7% for Pulmonology ward) were associated with particularly high bed-days of hospitalization, at approximately +15 days and +12 days on Geriatric and Pulmonology wards, respectively. Both wards showed marked seasonality for respiratory infections with winter peaks.
Conclusion: Real-world data showed that secondary diagnosed infections in aging adults imposed a high burden on hospital care along with longer hospital stays. This hampered bed availability during peak seasons.
Keywords: aging adults; geriatrics; hospitalization; infectious disease; pulmonology.
© 2022 De Cock, Strens, Van Osta and Standaert.
Conflict of interest statement
BS is employed by HEBO. DS is employed by Realidad. BS has received consultancy fees, unrelated to the present work, from GSK Vaccines, Biondvax, and Evidera-PMM. DS received a consultancy fee from GSK Vaccines to initiate the study in 2019. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Pilotto A, Veronese N, Daragjati J, Cruz-Jentoft AJ, Polidori MC, Mattace-Raso F, et al. Using the multidimensional prognostic index to predict clinical outcomes of hospitalized older persons: a prospective, multicenter, international study. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. (2019) 74(10):1643–9. 10.1093/gerona/gly239 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

