(E)-3-{4,6-Dimeth-oxy-2-[(E)-4-meth-oxy-styr-yl]-3-methyl-phen-yl}-1-(2-hy-droxy-5-meth-oxy-phen-yl)prop-2-en-1-one
- PMID: 36340611
- PMCID: PMC9462233
- DOI: 10.1107/S2414314620007920
(E)-3-{4,6-Dimeth-oxy-2-[(E)-4-meth-oxy-styr-yl]-3-methyl-phen-yl}-1-(2-hy-droxy-5-meth-oxy-phen-yl)prop-2-en-1-one
Abstract
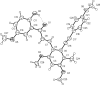
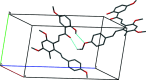
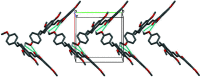
In the title compound, C28H28O6, the benzene rings in the resveratrol moiety are connected by a trans C=C double bond, and the hydroxyl group containing a benzene ring and the central benzene ring are linked through a C=(O)-C=C (enone) moiety to form a chalcone unit. An intra-molecular O-H⋯O hydrogen bond generates an S(6) ring motif. In the crystal, pairs of C-H⋯O hydrogen bonds generate dimers and additional weak C-H⋯O inter-actions link the dimers into chains propagating along the b-axis direction.
Keywords: C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds; chalcone; crystal structure; resveratrol.
© Yoo and Koh 2020.
Figures
References
-
- Bruker (2012). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS, Bruker AXS Inc. Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
-
- Gil, H. N., Koh, D., Lim, Y., Lee, Y. H. & Shin, S. Y. (2018). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 28, 2969–2975. - PubMed
-
- Lee, D. H., Jung Jung, Y., Koh, D., Lim, Y., Lee, Y. H. & Shin, S. Y. (2016). Cancer Lett. 372, 1–9. - PubMed
-
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. - PubMed
-
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
