Antibiotic prescribing patterns among patients admitted to an academic teaching hospital for COVID-19 during the first wave of the pandemic in Toronto: A retrospective, controlled study
- PMID: 36340852
- PMCID: PMC9603018
- DOI: 10.3138/jammi-2021-0020
Antibiotic prescribing patterns among patients admitted to an academic teaching hospital for COVID-19 during the first wave of the pandemic in Toronto: A retrospective, controlled study
Abstract
Background: Empirical antibiotics are not recommended for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).
Methods: In this retrospective study, patients admitted to Toronto General Hospital's general internal medicine from the emergency department for COVID-19 between March 1 and August 31, 2020 were compared with those admitted for community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) in 2020 and 2019 in the same months. The primary outcome was antibiotics use pattern: prevalence and concordance with COVID-19 or CAP guidelines. The secondary outcome was antibiotic consumption in days of therapy (DOT)/100 patient-days. We extracted data from electronic medical records. We used logistic regression to model the association between disease and receipt of antibiotics, linear regression to compare DOT.
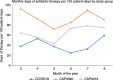
Results: The COVID-19, CAP 2020, and CAP 2019 groups had 67, 73, and 120 patients, respectively. Median age was 71 years; 58.5% were male. Prevalence of antibiotic use was 70.2%, 97.3%, and 90.8% for COVID-19, CAP 2020, and CAP 2019, respectively. Compared with CAP 2019, the adjusted odds ratio (aOR) for receiving antibiotics was 0.23 (95% CI 0.10 to 0.53, p = 0.001) and 3.42 (95% CI 0.73 to 15.95, p = 0.117) for COVID-19 and CAP 2020, respectively. Among patients receiving antibiotics within 48 hours of admission, compared with CAP 2019, the aOR for guideline-concordant combination regimens was 2.28 (95% CI 1.08 to 4.83, p = 0.031) for COVID-19, and 1.06 (95% CI 0.55 to 2.05, p = 0.856) for CAP 2020. Difference in mean DOT/100 patient-days was -24.29 (p = 0.009) comparing COVID-19 with CAP 2019, and +28.56 (p = 0.003) comparing CAP 2020 with CAP 2019.
Conclusions: There are opportunities for antimicrobial stewardship to address unnecessary antibiotic use.
Historique: L’antibiothérapie empirique n’est pas recommandée pour le traitement de la maladie à coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19).
Méthodologie: Dans cette étude rétrospective, les chercheurs ont comparé les patients atteints de COVID-19 hospitalisés au département de médecine interne générale du Toronto General Hospital entre le 1er mars et le 31 août 2020 après être passés par l’urgence à ceux hospitalisés à cause d’une pneumonie d’origine communautaire (POC) au cours des mêmes mois en 2020 et 2019 (POC-20 et POC-19). Le résultat primaire était le schéma d’utilisation des antibiotiques, c’est-à-dire la prévalence et le respect des lignes directrices sur la COVID-19 ou la POC. Le résultat secondaire correspondait à la consommation d’antibiotiques pendant les jours de traitement (JdT)/100 jours-patients. Les chercheurs ont puisé les données dans les dossiers médicaux électroniques. Ils se sont servi de la régression logistique pour modéliser l’association entre la maladie et la réception des antibiotiques, et de la régression linéaire pour comparer les JdT.
Résultats: Le groupe COVID-19, le groupe POC-20 et le groupe POC-19 étaient composés de 67, 73 et 120 patients, respectivement. Ils avaient un âge médian de 71 ans, et 58,5 % étaient de sexe masculin. La prévalence d’utilisation d’antibiotiques s’élevait à 70,2 %, 97,3 % et 90,8 % dans les groupes COVID-19, POC-20 et POC-19, respectivement. Par rapport au groupe POC-19, le rapport de cotes rajusté (RCr) relatif à la réception d’antibiotiques s’élevait à 0,23 (IC à 95 %, 0,10 à 0,53, p = 0,001) et 3,42 (IC à 95 %, 0,73 à 15,95, p = 0,117) dans les groupes COVID-19 et POC-20, respectivement. Chez les patients qui avaient reçu des antibiotiques dans les 48 heures suivant leur hospitalisation par rapport au POC-19, le RCr relatif à la posologie d’association conforme aux lignes directrices était de 2,28 (IC à 95 %, 1,08 à 4,83, p = 0,031) et de 1,06 (IC à 95 %, 0,55 à 2,05, p = 0,856) dans le groupe POC-20. La différence quant au nombre moyen de JdT/100 jours-patients correspondait à –24,29 (p = 0,009) lorsqu’on comparait le groupe COVID-19 au groupe POC-19, et à +28,56 (p = 0,003) lorsqu’on comparait le groupe POC-20 au groupe POC-19.
Conclusions: L’utilisation inutile d’antibiotiques pourrait très bien être prise en charge par la gérance des antimicrobiens.
Keywords: COVID-19; antibiotics; community-acquired pneumonia; stewardship.
Copyright © 2022, Association of Medical Microbiology and Infectious Disease Canada (AMMI Canada).
Conflict of interest statement
M So is the Chair of the Canadian Society of Hospital Pharmacists Foundation Education Grant Review Committee.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ambulatory Antibiotic Prescribing for Children with Pneumonia After Publication of National Guidelines: A Cross-Sectional Retrospective Study.Infect Dis Ther. 2020 Mar;9(1):69-76. doi: 10.1007/s40121-019-00276-3. Epub 2019 Nov 27. Infect Dis Ther. 2020. PMID: 31776843 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of an emergency medicine pharmacist on empiric antibiotic prescribing for pneumonia and intra-abdominal infections.Am J Emerg Med. 2019 May;37(5):839-844. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2018.07.052. Epub 2018 Jul 29. Am J Emerg Med. 2019. PMID: 30097272
-
Variability in Antibiotic Prescribing for Community-Acquired Pneumonia.Pediatrics. 2017 Apr;139(4):e20162331. doi: 10.1542/peds.2016-2331. Epub 2017 Mar 7. Pediatrics. 2017. PMID: 28270546 Free PMC article.
-
Guideline-concordant antibiotic use and survival among patients with community-acquired pneumonia admitted to the intensive care unit.Clin Ther. 2010 Feb;32(2):293-9. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2010.02.006. Clin Ther. 2010. PMID: 20206787
-
Antibiotic stewardship in community-acquired pneumonia.Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2017 Apr;15(4):351-359. doi: 10.1080/14787210.2017.1274232. Epub 2016 Dec 27. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2017. PMID: 28002979 Review.
Cited by
-
Trends in hospital antibiotic utilization during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic: A multicenter interrupted time-series analysis.Antimicrob Steward Healthc Epidemiol. 2022 Jul 28;2(1):e128. doi: 10.1017/ash.2022.268. eCollection 2022. Antimicrob Steward Healthc Epidemiol. 2022. PMID: 36483375 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous