Study of Association of Global Deoxyribonucleic Acid Methylation in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
- PMID: 36341021
- PMCID: PMC9635373
- DOI: 10.4103/jhrs.jhrs_64_22
Study of Association of Global Deoxyribonucleic Acid Methylation in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
Abstract
Background: Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), a common endocrine disorder affecting 5%-10% of reproductive age women worldwide, associated with various metabolic morbidities. One potential molecular mechanism could be epigenetic modifications, such as deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) methylation.
Aims: The aim is to determine the association of global DNA methylation in peripheral blood leucocyte (PBL) cells and PCOS women. Also to assess abnormal lipid profile, insulin resistance, gonadotropins and reproductive markers in them.
Settings and design: The study design involves a hospital-based prospective case-control study.
Materials and methods: Fifty women with PCOS, diagnosed as per Rotterdam criteria and the rest 50 without PCOS or any disease, attending outpatient department were recruited. Serum biochemical markers and Global DNA methylation assay were done by using standardised kit.
Statistical analysis used: Data were compared using Independent t-test or Mann-Whitney U test using IBM SPSS version 26.0. P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
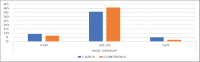
Results: Majority, 72% of PCOS and 82% non-PCOS women were between 20 and 25 years. Most common presenting symptom was menstrual irregularity. Women with PCOS have high serum cholesterol and triglyceride level, elevated serum luteinising hormone (LH), follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), LH/FSH ratio and testosterone but low estradiol levels as compared to non-PCOS. Statistically significant high mean Global DNA methylation percentage was found in PBLs of women with PCOS.
Conclusion: Despite study limitations, this study provided insight into Global DNA methylation in PBLs was associated with PCOS. It requires further research to better understand the influence of epigenetic factors including genome-wide DNA methylation profiling in PCOS development.
Keywords: Epigenetic; global deoxyribonucleic acid methylation; polycystic ovary syndrome.
Copyright: © 2022 Journal of Human Reproductive Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bozdag G, Mumusoglu S, Zengin D, Karabulut E, Yildiz BO. The prevalence and phenotypic features of polycystic ovary syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Hum Reprod. 2016;31:2841–55. - PubMed
-
- Krysiak R, Okopień B, Gdula-Dymek A, Herman ZS. Update on the management of polycystic ovary syndrome. Pharmacol Rep. 2006;58:614–25. - PubMed
-
- Hardiman P, Pillay OC, Atiomo W. Polycystic ovary syndrome and endometrial carcinoma. Lancet. 2003;361:1810–2. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources