Best practices for multi-ancestry, meta-analytic transcriptome-wide association studies: Lessons from the Global Biobank Meta-analysis Initiative
- PMID: 36341024
- PMCID: PMC9631681
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xgen.2022.100180
Best practices for multi-ancestry, meta-analytic transcriptome-wide association studies: Lessons from the Global Biobank Meta-analysis Initiative
Abstract
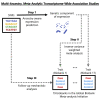
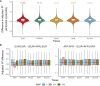
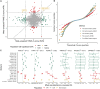
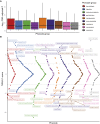
The Global Biobank Meta-analysis Initiative (GBMI), through its diversity, provides a valuable opportunity to study population-wide and ancestry-specific genetic associations. However, with multiple ascertainment strategies and multi-ancestry study populations across biobanks, GBMI presents unique challenges in implementing statistical genetics methods. Transcriptome-wide association studies (TWASs) boost detection power for and provide biological context to genetic associations by integrating genetic variant-to-trait associations from genome-wide association studies (GWASs) with predictive models of gene expression. TWASs present unique challenges beyond GWASs, especially in a multi-biobank, meta-analytic setting. Here, we present the GBMI TWAS pipeline, outlining practical considerations for ancestry and tissue specificity, meta-analytic strategies, and open challenges at every step of the framework. We advise conducting ancestry-stratified TWASs using ancestry-specific expression models and meta-analyzing results using inverse-variance weighting, showing the least test statistic inflation. Our work provides a foundation for adding transcriptomic context to biobank-linked GWASs, allowing for ancestry-aware discovery to accelerate genomic medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Grants and funding
- R01 GM140287/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG011138/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HG010464/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG006399/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA251555/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA244670/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K99 HG012222/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG009120/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI153827/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AG068026/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R35 HG010718/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH115676/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH126459/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG009086/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG011715/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

