The correlation of temporal changes of neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio with seizure severity and the following seizure tendency in patients with epilepsy
- PMID: 36341114
- PMCID: PMC9630561
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2022.964923
The correlation of temporal changes of neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio with seizure severity and the following seizure tendency in patients with epilepsy
Abstract
Background: Changes in the neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) has been reported to be associated with epilepsy. Here we aim to investigate the correlation of temporal changes of NLR level with seizure severity and the follow-up seizure attacks in patients with epilepsy (PWE).
Methods: We performed a retrospective analysis of the laboratory data including leukocyte count and NLR within 24 h of acute seizure and during the follow-up period of 5-14 days after acute seizure (NLR1, NLR2, respectively) in 115 PWE, and 98 healthy individuals were included as controls in this study. The correlation of laboratory data with seizure types, etiology of epilepsy, anti-seizure drugs (ASDs), seizure severity, and the follow-up seizure attacks in PWE was studied.
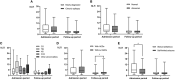
Results: Leukocyte count (P < 0.001) and NLR level (P < 0.001) were found significantly different between PWE and controls. On the other hand, a multivariable logistic regression analysis showed that NLR1 level (OR = 2.992, P = 0.001) and admission leukocyte (OR = 2.307, P = 0.002) were both independently associated with acute epileptic seizures. Especially, higher NLR1 level was significantly associated with status epileptics (P = 0.013) and recurrent seizures after admission (P < 0.001). Furthermore, the multivariable logistic regression analysis indicated that higher NLR1 was a predictor for the tendency of the following recurrent seizure attacks (OR = 1.144, P = 0.002). NLR2 was inversely correlated with ASDs taken (P = 0.011). Levels of NLR1 (r = 0.441, P < 0.001) and NLR2 (r = 0.241, P = 0.009) were both positively correlated with seizure severity.
Conclusions: Seizures were correlated with the alterations of systemic inflammation reflected by leukocyte and NLR. NLR1 and admission leukocyte were both independently associated with acute epileptic seizures. Higher NLR1 was associated with status epilepticus and independently predicted the tendency of the following epileptic seizures. NLR2 was significantly associated with ASDs taken. Besides, NLR may be used as a biomarker for seizure severity.
Keywords: inflammation; neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio; recurrent seizure attacks; seizure severity; status epilepticus.
Copyright © 2022 Li, Yang, Hu, Cao, Ding, Sun, Li, Liu, Xu and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

