Machine Learning Models for Predicting the Risk of Hard-to-Heal Diabetic Foot Ulcers in a Chinese Population
- PMID: 36341229
- PMCID: PMC9628710
- DOI: 10.2147/DMSO.S383960
Machine Learning Models for Predicting the Risk of Hard-to-Heal Diabetic Foot Ulcers in a Chinese Population
Abstract
Background: Early detection of hard-to-heal diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs) is vital to prevent a poor prognosis. The purpose of this work was to employ clinical characteristics to create an optimal predictive model of hard-to-heal DFUs (failing to decrease by >50% at 4 weeks) based on machine learning algorithms.
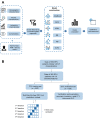
Methods: A total of 362 DFU patients hospitalized in two tertiary hospitals in eastern China were enrolled in this study. The training dataset and validation dataset were split at a ratio of 7:3. Univariate logistic analysis and clinical experience were utilized to screen clinical characteristics as predictive features. The following six machine learning algorithms were used to build prediction models for differentiating hard-to-heal DFUs: support vector machine, the naïve Bayesian (NB) model, k-nearest neighbor, general linear regression, adaptive boosting, and random forest. Five cross-validations were employed to realize the model's parameters. Accuracy, precision, recall, F1-scores, and AUCs were utilized to compare and evaluate the models' efficacy. On the basis of the best model identified, the significance of each characteristic was evaluated, and then an online calculator was developed.
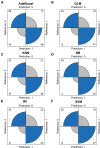
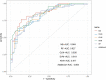
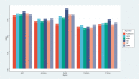
Results: Independent predictors for model establishment included sex, insulin use, random blood glucose, wound area, diabetic retinopathy, peripheral arterial disease, smoking history, serum albumin, serum creatinine, and C-reactive protein. After evaluation, the NB model was identified as the most generalizable model, with an AUC of 0.864, a recall of 0.907, and an F1-score of 0.744. Random blood glucose, C-reactive protein, and wound area were determined to be the three most important influencing factors. A corresponding online calculator was created (https://predicthardtoheal.azurewebsites.net/).
Conclusion: Based on clinical characteristics, machine learning algorithms can achieve acceptable predictions of hard-to-heal DFUs, with the NB model performing the best. Our online calculator can assist doctors in identifying the possibility of hard-to-heal DFUs at the time of admission to reduce the likelihood of a dismal prognosis.
Keywords: classification; diabetic foot ulcers; hard-to-heal; machine learning.
© 2022 Wang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Machine learning for the prediction of minor amputation in University of Texas grade 3 diabetic foot ulcers.PLoS One. 2022 Dec 6;17(12):e0278445. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0278445. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36472981 Free PMC article.
-
An interpreting machine learning models to predict amputation risk in patients with diabetic foot ulcers: a multi-center study.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025 Mar 25;16:1526098. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1526098. eCollection 2025. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40201760 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing diabetic foot ulcer prediction with machine learning: A focus on Localized examinations.Heliyon. 2024 Sep 19;10(19):e37635. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37635. eCollection 2024 Oct 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39386877 Free PMC article.
-
Which biomarkers predict hard-to-heal diabetic foot ulcers? A scoping review.Drug Discov Ther. 2024 Jan 12;17(6):368-377. doi: 10.5582/ddt.2023.01086. Epub 2023 Dec 22. Drug Discov Ther. 2024. PMID: 38143075
-
Advancing pharmacotherapy for diabetic foot ulcers.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2019 Jun;20(9):1153-1160. doi: 10.1080/14656566.2019.1598378. Epub 2019 Apr 8. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 30958725 Review.
Cited by
-
Protocol for metadata and image collection at diabetic foot ulcer clinics: enabling research in wound analytics and deep learning.Biomed Eng Online. 2024 Jan 29;23(1):12. doi: 10.1186/s12938-024-01210-6. Biomed Eng Online. 2024. PMID: 38287324 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of risk factors and predictive value of a nomogram model for sepsis in patients with diabetic foot.World J Diabetes. 2025 Apr 15;16(4):104088. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i4.104088. World J Diabetes. 2025. PMID: 40236852 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial Intelligence Methods for Diagnostic and Decision-Making Assistance in Chronic Wounds: A Systematic Review.J Med Syst. 2025 Feb 19;49(1):29. doi: 10.1007/s10916-025-02153-8. J Med Syst. 2025. PMID: 39969674 Free PMC article.
-
A machine learning approach to predict foot care self-management in older adults with diabetes.Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2024 Oct 7;16(1):244. doi: 10.1186/s13098-024-01480-z. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2024. PMID: 39375790 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

