Comparison of different types of therapy for overactive bladder: A systematic review and network meta-analysis
- PMID: 36341256
- PMCID: PMC9633225
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2022.1014291
Comparison of different types of therapy for overactive bladder: A systematic review and network meta-analysis
Abstract
To compare the efficacy and safety of different interventions [including antimuscarinics, mirabegron, OnabotulinumtoxinA, sacral neuromodulation (SNM) and peripheral tibial nerve stimulation (PTNS)] for treating idiopathic overactive bladder (OAB). PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, and other sources were searched for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) comparing interventions for overactive bladder from 1 January 2000 to 19 April 2021. A systematic review and network meta-analysis were performed by two authors independently. Fifty-five RCTs involving 32,507 patients were included in this analysis. Overall, antimuscarinics, mirabegron, OnabotulinumtoxinA, sacral neuromodulation, and peripheral tibial nerve stimulation were more efficacious than placebo, and sacral neuromodulation showed the best effect for reducing micturition frequency, urgency episodes and urgency urinary incontinence episodes. OnabotulinumtoxinA was the best intervention for achieving reductions of 100 and ≥50% in the number of urinary incontinence episodes/day, and peripheral tibial nerve stimulation was the best intervention for reducing urinary incontinence episodes. Antimuscarinics, mirabegron and peripheral tibial nerve stimulation had a similar efficacy for reducing micturition frequency, urinary incontinence episodes and urgency urinary incontinence episodes. The results revealed that all interventions examined herein were efficacious for managing adult overactive bladder syndrome compared with placebo. Furthermore, sacral neuromodulation and OnabotulinumtoxinA were the most efficient treatments for overactive bladder.
Systematic review registration: [https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/display_record.php?RecordID=251966], identifier [CRD42021251966].
Keywords: antimuscarinics; mirabegron; network meta-analysis; overactive bladder; peripheral tibial nerve stimulation; sacral neuromodulation (SNM).
Copyright © 2022 Liu, Li, Shi, Zhang and Guo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


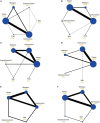
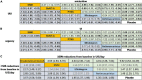
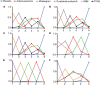
Similar articles
-
Comparative Efficacy of Neuromodulation Technologies for Overactive Bladder in Adults: A Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Neuromodulation. 2023 Dec;26(8):1535-1548. doi: 10.1016/j.neurom.2022.06.004. Epub 2022 Aug 18. Neuromodulation. 2023. PMID: 35989159 Review.
-
What Are the Short-term Benefits and Potential Harms of Therapeutic Modalities for the Management of Overactive Bladder Syndrome in Women? A Review of Evidence Under the Auspices of the European Association of Urology, Female Non-neurogenic Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Guidelines Panel.Eur Urol. 2023 Sep;84(3):302-312. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2023.05.014. Epub 2023 Jun 17. Eur Urol. 2023. PMID: 37331921 Review.
-
Beyond Antimuscarinics: A Review of Pharmacological and Interventional Options for Overactive Bladder Management in Men.Eur Urol. 2021 Apr;79(4):492-504. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2020.12.032. Epub 2021 Jan 2. Eur Urol. 2021. PMID: 33402296
-
Non-inferior and more feasible transcutaneous tibial nerve stimulation in treating overactive bladder: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Int J Urol. 2022 Oct;29(10):1170-1180. doi: 10.1111/iju.14961. Epub 2022 Jun 16. Int J Urol. 2022. PMID: 35711082
-
OnabotulinumtoxinA vs Sacral Neuromodulation on Refractory Urgency Urinary Incontinence in Women: A Randomized Clinical Trial.JAMA. 2016 Oct 4;316(13):1366-1374. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.14617. JAMA. 2016. PMID: 27701661 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Long-Term Surveillance and Management of Urological Complications in Chronic Spinal Cord-Injured Patients.J Clin Med. 2022 Dec 9;11(24):7307. doi: 10.3390/jcm11247307. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 36555924 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effectiveness of simultaneous electroacupuncture stimulation on the tibial and ilioinguinal-iliohypogastric nerves in the treatment of refractory overactive bladder syndrome in women.Curr Urol. 2025 Mar;19(2):110-116. doi: 10.1097/CU9.0000000000000266. Epub 2025 Jan 21. Curr Urol. 2025. PMID: 40314016 Free PMC article.
-
Lower urinary tract dysfunction in the central nervous system neurogenic bladder and the real-life treatment outcome of botulinum toxin A.Tzu Chi Med J. 2024 May 24;36(3):260-270. doi: 10.4103/tcmj.tcmj_29_24. eCollection 2024 Jul-Sep. Tzu Chi Med J. 2024. PMID: 38993829 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Abnormal Resting-State Network Presence in Females with Overactive Bladder.Biomedicines. 2023 Jun 5;11(6):1640. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11061640. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37371735 Free PMC article.
-
Invasive urodynamic investigations in the management of women with refractory overactive bladder symptoms: FUTURE, a superiority RCT and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2025 Jul;29(27):1-139. doi: 10.3310/UKYW4923. Health Technol Assess. 2025. PMID: 40620147 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

