PET/CT molecular imaging in the era of immune-checkpoint inhibitors therapy
- PMID: 36341331
- PMCID: PMC9630646
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1049043
PET/CT molecular imaging in the era of immune-checkpoint inhibitors therapy
Abstract
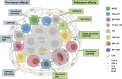
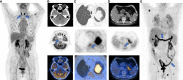
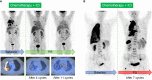
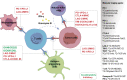
Cancer immunotherapy, especially immune-checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), has paved a new way for the treatment of many types of malignancies, particularly advanced-stage cancers. Accumulating evidence suggests that as a molecular imaging modality, positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) can play a vital role in the management of ICIs therapy by using different molecular probes and metabolic parameters. In this review, we will provide a comprehensive overview of the clinical data to support the importance of 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose PET/CT (18F-FDG PET/CT) imaging in the treatment of ICIs, including the evaluation of the tumor microenvironment, discovery of immune-related adverse events, evaluation of therapeutic efficacy, and prediction of therapeutic prognosis. We also discuss perspectives on the development direction of 18F-FDG PET/CT imaging, with a particular emphasis on possible challenges in the future. In addition, we summarize the researches on novel PET molecular probes that are expected to potentially promote the precise application of ICIs.
Keywords: immune-checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs); metabolic parameter; molecular imaging; molecular probe; positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT); tumor microenvironment (TME).
Copyright © 2022 Gao, Wu, Chen, Ma, Zhang, Chen, Liao and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The value of FDG PET/CT imaging in outcome prediction and response assessment of lymphoma patients treated with immunotherapy: a meta-analysis and systematic review.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2022 Nov;49(13):4661-4676. doi: 10.1007/s00259-022-05918-2. Epub 2022 Aug 6. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2022. PMID: 35932329 Free PMC article.
-
Interpretation of 2-[18F]FDG PET/CT in Hodgkin lymphoma patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors.Eur Radiol. 2022 Sep;32(9):6536-6544. doi: 10.1007/s00330-022-08669-8. Epub 2022 Mar 28. Eur Radiol. 2022. PMID: 35344061 Review.
-
Imaging the Cancer Immune Environment and Its Response to Pharmacologic Intervention, Part 2: The Role of Novel PET Agents.J Nucl Med. 2020 Nov;61(11):1553-1559. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.120.248823. Epub 2020 Sep 4. J Nucl Med. 2020. PMID: 32887755
-
Prognostic value of 18F-FDG PET/CT in patients with advanced or metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Immunol. 2022 Nov 17;13:1014063. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1014063. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36466905 Free PMC article.
-
Immune PET Imaging.Radiol Clin North Am. 2021 Sep;59(5):875-886. doi: 10.1016/j.rcl.2021.05.010. Radiol Clin North Am. 2021. PMID: 34392924 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Is 18F-FDG-PET/CT an Optimal Imaging Modality for Detecting Immune-Related Adverse Events after Immune-Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy? Pros and Cons.Cancers (Basel). 2024 May 24;16(11):1990. doi: 10.3390/cancers16111990. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38893111 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular MRI of T-cell immune response to cryoablation in immunologically hot vs. cold hepatocellular carcinoma.JHEP Rep. 2024 Dec 4;7(3):101294. doi: 10.1016/j.jhepr.2024.101294. eCollection 2025 Mar. JHEP Rep. 2024. PMID: 40028344 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts: Heterogeneity, Cancer Pathogenesis, and Therapeutic Targets.MedComm (2020). 2025 Jul 11;6(7):e70292. doi: 10.1002/mco2.70292. eCollection 2025 Jul. MedComm (2020). 2025. PMID: 40656546 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prediction of pathological response to neoadjuvant immunochemotherapy with baseline and post-treatment 18F-FDG PET imaging biomarkers in patients with locally advanced gastric cancer.BMC Cancer. 2025 Feb 28;25(1):378. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-13765-1. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40022087 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting of immune checkpoint regulator V-domain Ig suppressor of T-cell activation (VISTA) with 89Zr-labelled CI-8993.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2024 Nov;51(13):3863-3873. doi: 10.1007/s00259-024-06854-z. Epub 2024 Jul 26. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2024. PMID: 39060374 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

