Negative regulator NLRC3: Its potential role and regulatory mechanism in immune response and immune-related diseases
- PMID: 36341336
- PMCID: PMC9630602
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1012459
Negative regulator NLRC3: Its potential role and regulatory mechanism in immune response and immune-related diseases
Abstract
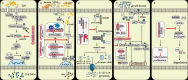
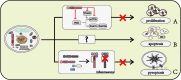
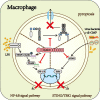
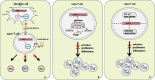
NLRC3 is a member of the pattern recognition receptors nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain (NOD)-like receptors (NLRs) family, and plays a pivotal regulatory role in modulating the activation of immune cells. In macrophages, NLRC3 inhibits the activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway, the STING/TBK1 signaling pathway, and the formation of the inflammasome. In the context of T cells immune response, NLRC3 prevents the activation of T cells by regulating the function of dendritic cells and directly influencing the function of T cells. Different from other pattern recognition receptors, NLRC3 is more closely associated with regulatory activity than pathogens recognition, it influences the fates of cells, for example, prevents proliferation, promotes apoptosis and inhibits pyroptosis. These cellular functions regulated by NLRC3 are involved in the development processes of a variety of diseases, such as infectious disease, sterile inflammatory diseases, and cancer. However, its characteristics, function and regulatory mechanism in immune response and immune-related diseases have not been addressed fully. In this review, we elaborate the potential roles of NLRC3 from several different levels, include molecular mechanism, cellular functions in the immune-related diseases.
Keywords: NF-κB; NLRC3; NOD-like receptor; PI3K; immune response; immune-related diseases; pyroptosis; sting.
Copyright © 2022 Sun, Xu, Zhang, Song, Gao, He and Shang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Overview of the anti-inflammatory function of the innate immune sensor NLRC3.Mol Immunol. 2023 Jan;153:36-41. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2022.11.014. Epub 2022 Nov 17. Mol Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36403432 Review.
-
NLRC3 protein inhibits inflammation by disrupting NALP3 inflammasome assembly via competition with the adaptor protein ASC for pro-caspase-1 binding.J Biol Chem. 2017 Jul 28;292(30):12691-12701. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.769695. Epub 2017 Jun 5. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28584053 Free PMC article.
-
Focus on negatively regulated NLRs in inflammation and cancer.Int Immunopharmacol. 2024 Jul 30;136:112347. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.112347. Epub 2024 May 30. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38820966 Review.
-
NLRC3 regulates cellular proliferation and apoptosis to attenuate the development of colorectal cancer.Cell Cycle. 2017 Jul 3;16(13):1243-1251. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2017.1317414. Epub 2017 Jun 9. Cell Cycle. 2017. PMID: 28598238 Free PMC article.
-
The expanding and function of NLRC3 or NLRC3-like in teleost fish: Recent advances and novel insights.Dev Comp Immunol. 2021 Jan;114:103859. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2020.103859. Epub 2020 Sep 5. Dev Comp Immunol. 2021. PMID: 32896535 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanism and Application Prospects of NLRC3 Regulating cGAS-STING Pathway in Lung Cancer Immunotherapy.Int J Med Sci. 2024 Oct 7;21(13):2613-2622. doi: 10.7150/ijms.102328. eCollection 2024. Int J Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 39439455 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Uncovering the Role of Anoikis-Related Genes in Modulating Immune Infiltration and Pathogenesis of Diabetic Kidney Disease.J Inflamm Res. 2024 Jul 24;17:4975-4991. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S446752. eCollection 2024. J Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 39070131 Free PMC article.
-
NLRC3 Attenuates Antiviral Innate Immune Response by Targeting IRF7 in Grass Carp (Ctenopharyngodon idelus).Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jan 20;26(2):840. doi: 10.3390/ijms26020840. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39859554 Free PMC article.
-
Signaling pathways in macrophages: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic targets.MedComm (2020). 2023 Sep 11;4(5):e349. doi: 10.1002/mco2.349. eCollection 2023 Oct. MedComm (2020). 2023. PMID: 37706196 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA-19b exacerbates systemic sclerosis through promoting Th9 cells.Cell Rep. 2024 Aug 27;43(8):114565. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114565. Epub 2024 Jul 30. Cell Rep. 2024. PMID: 39083380 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

