The beneficial effects of Lacticaseibacillus casei on the small intestine and colon of Swiss mice against the deleterious effects of 5-fluorouracil
- PMID: 36341441
- PMCID: PMC9635922
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.954885
The beneficial effects of Lacticaseibacillus casei on the small intestine and colon of Swiss mice against the deleterious effects of 5-fluorouracil
Abstract
Background: Intestinal mucositis is one of the most common and important side effects of 5-fluorouracil (5-FU). Currently, there are still no specific and effective protocols for its prevention and treatment. The aim of the present study was to evaluate the effect of oral administration of Lacticaseibacillus casei (L. casei) on the progression of 5-FU-induced intestinal mucositis. Methods: L. casei (1x109 CFU/ml) or saline was orally administered to Swiss mice, beginning 15 days before intestinal mucositis induction by single intraperitoneal 5-FU administration (450 mg/kg). Body weight, number of peripheral leukocytes and fecal lactic acid bacteria were monitored. After euthanasia, on day 18, tissue samples from colon and each small intestine segment were collected for histopathology. Jejunal tissues were collected and evaluated for iNOS and TNF-alpha immunoexpression, IL-1-beta, IL-6 and TNF-alpha levels, malonaldehyde (MDA) accumulation, invertase activity and factor nuclear kappa B (NFkB-P65) gene expression, toll like receptor-4 (TLR-4), mucin-2 (MUC-2), occludin and zonula occludens-1 (ZO-1).
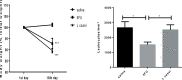
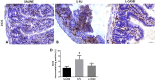
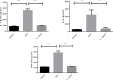
Results: The positive impact of L. casei on 5-FU-induced leukopenia was observed, but not on 5-FU-induced weight loss in mice. L. casei reduced 5-FU-induced inflammation in the colon and small intestine (p<0.05). Decreased TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6 (p<0.05) and MDA (p<0.05) levels, as well as decreased iNOS and TNF-alpha protein expressions (p<0.05) were found in the jejunum from L casei group. In addition, L-casei down-regulated NFKB-P65 (p<0.05) and TLR-4 (p<0.05) gene expressions and up-regulated MUC-2 and mucosal barrier proteins occludin and ZO-1 gene expressions (p<0.05). Furthermore, greater lactic acid bacteria population (p<0.05) was found in the L. casei group when compared to control groups.
Conclusion: Oral L. casei administration can protect the intestine of Swiss mice from 5-FU-induced intestinal mucositis, thus contributing to overall health.
Keywords: 5-fluorouracil; Lacticaseibacillus casei; chemotherapy; mucositis; probiotic.
Copyright © 2022 Barbosa, Oliveira, Ribeiro, de Medeiros, Lima, Guerra, de Araújo Júnior, de Sousa Junior, Martins, Paiva, Andrade, Rebouças, Brito, Leitâo and de Araújo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Lacticaseibacillus casei decrease long-chain fatty acids and most substances in an experimental model of intestinal mucositis.Acta Cir Bras. 2023 Dec 1;38:e386723. doi: 10.1590/acb386723. eCollection 2023. Acta Cir Bras. 2023. PMID: 38055402 Free PMC article.
-
Amelioration of Chemotherapy-Induced Intestinal Mucositis by Orally Administered Probiotics in a Mouse Model.PLoS One. 2015 Sep 25;10(9):e0138746. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0138746. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26406888 Free PMC article.
-
Wumei pills attenuates 5-fluorouracil-induced intestinal mucositis through Toll-like receptor 4/myeloid differentiation factor 88/nuclear factor-κB pathway and microbiota regulation.World J Gastroenterol. 2022 Aug 28;28(32):4574-4599. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i32.4574. World J Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 36157934 Free PMC article.
-
Administration of probiotic mixture DM#1 ameliorated 5-fluorouracil-induced intestinal mucositis and dysbiosis in rats.Nutrition. 2017 Jan;33:96-104. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2016.05.003. Epub 2016 May 20. Nutrition. 2017. PMID: 27427511
-
Protective Effects of Spondias mombin L. Juice Alone or in Combination With Lactobacillus acidophilus in 5-Fluorouracil-Induced Experimental Intestinal Mucositis.Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2024 Dec 31:e14970. doi: 10.1111/nmo.14970. Online ahead of print. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2024. PMID: 39739321
Cited by
-
Probiotics and Probiotic-like Agents against Chemotherapy-Induced Intestinal Mucositis: A Narrative Review.J Pers Med. 2023 Oct 12;13(10):1487. doi: 10.3390/jpm13101487. J Pers Med. 2023. PMID: 37888098 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microbiota-Accessible Boron-Containing Compounds in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome.Medicina (Kaunas). 2023 Nov 7;59(11):1965. doi: 10.3390/medicina59111965. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023. PMID: 38004014 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oral administration of Lactobacillus casei DG® after ileostomy closure in restorative proctocolectomy: a randomized placebo-controlled trial (microbiota and immune microenvironment in pouchitis -MEP1).Gut Microbes. 2024 Jan-Dec;16(1):2423037. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2024.2423037. Epub 2024 Nov 1. Gut Microbes. 2024. PMID: 39485259 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effectiveness of Probiotic Therapy in the Management of PeriodontalDisease in Diabetic Patients: A Scoping Review.Curr Diabetes Rev. 2024;20(9):e281123223961. doi: 10.2174/0115733998271193231108054254. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2024. PMID: 38018184
-
Lacticaseibacillus casei decrease long-chain fatty acids and most substances in an experimental model of intestinal mucositis.Acta Cir Bras. 2023 Dec 1;38:e386723. doi: 10.1590/acb386723. eCollection 2023. Acta Cir Bras. 2023. PMID: 38055402 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

