Protectins: Their biosynthesis, metabolism and structure-functions
- PMID: 36341938
- PMCID: PMC9838224
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bcp.2022.115330
Protectins: Their biosynthesis, metabolism and structure-functions
Abstract
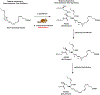
Several lipoxygenase enzymes and cyclooxygenase-2 stereoselectively convert the polyunsaturated fatty acids arachidonic acid, eicosapentaenoic acid, docosahexaenoic acid, and n-3 docosapentaenoic acid into numerous oxygenated products. Biosynthetic pathway studies have shown, during the resolution phase of acute inflammation, that distinct families of endogenous products are formed. These products were named specialized pro-resolving mediators, given their specialized functions in the inflammation-resolution circuit, enhancing the return of inflamed and injured tissue to homeostasis. The lipoxins, resolvins, protectins and maresins, together with the sulfido-conjugates of the resolvins, protectins and maresins, constitute the four individual families of these local mediators. When administrated in vivo in a wide range of human disease models, the specialized pro-resolving mediators display potent bioactions. The detailed and individual biosynthetic steps constituting the biochemical pathways, the metabolism, recent reports on structure-function studies and pharmacodynamic data of the protectins, are presented herein. Emphasis is on the structure-function results on the recent members of the sulfido conjugated protectins and further metabolism of protectin D1. Moreover, the members of the individual families of specialized pro-resolving mediators and their biosynthetic precursor are presented. Today 43 specialized pro-resolving mediators possessing pro-resolution and anti-inflammatory bioactions are reported and confirmed, constituting a basis for resolution pharmacology. This emerging biomedical field provides a new approach for drug discovery, that is also discussed.
Keywords: Biosynthesis; Cyclooxygenase-2; Lipoxygenases; Protectins; Resolution pharmacology; Specialized pro-resolving mediators.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
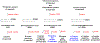


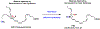

Similar articles
-
The biosynthetic pathways of the protectins.Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2023 Dec;169:106787. doi: 10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2023.106787. Epub 2023 Oct 6. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2023. PMID: 37806439 Review.
-
The novel lipid mediator PD1n-3 DPA: An overview of the structural elucidation, synthesis, biosynthesis and bioactions.Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2017 Nov;133:103-110. doi: 10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2017.06.003. Epub 2017 Jun 7. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2017. PMID: 28602942 Free PMC article. Review.
-
E-series resolvin metabolome, biosynthesis and critical role of stereochemistry of specialized pro-resolving mediators (SPMs) in inflammation-resolution: Preparing SPMs for long COVID-19, human clinical trials, and targeted precision nutrition.Semin Immunol. 2022 Jan;59:101597. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2022.101597. Epub 2022 Feb 16. Semin Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35227568 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protectins and maresins: New pro-resolving families of mediators in acute inflammation and resolution bioactive metabolome.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Apr;1851(4):397-413. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2014.08.006. Epub 2014 Aug 17. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25139562 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biology and Total Synthesis of n-3 Docosapentaenoic Acid-Derived Specialized Pro-Resolving Mediators.Molecules. 2024 Jun 14;29(12):2833. doi: 10.3390/molecules29122833. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38930898 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Inflammation resolution and specialized pro-resolving lipid mediators in chronic rhinosinusitis.Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2023 Jul-Dec;19(8):969-979. doi: 10.1080/1744666X.2023.2232554. Epub 2023 Jul 4. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37392068 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolization of Resolvin E4 by ω-Oxidation in Human Neutrophils: Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of 20-Hydroxy-Resolvin E4 (20-OH-RvE4).ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2023 Nov 20;6(12):1898-1908. doi: 10.1021/acsptsci.3c00201. eCollection 2023 Dec 8. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2023. PMID: 38093843 Free PMC article.
-
Resolvins and cysteinyl-containing pro-resolving mediators activate resolution of infectious inflammation and tissue regeneration.Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2023 Jun;166:106718. doi: 10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2023.106718. Epub 2023 Feb 21. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2023. PMID: 36813255 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stereoselective Synthesis, Pro-resolution, and Anti-inflammatory Actions of RvD5n-3 DPA.J Nat Prod. 2023 Nov 24;86(11):2546-2553. doi: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.3c00769. Epub 2023 Oct 25. J Nat Prod. 2023. PMID: 37879110 Free PMC article.
-
The profile of oxidative stress markers (arachidonic and linoleic acid derivatives) in patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia in relation to metabolic syndrome.Aging (Albany NY). 2025 Jan 6;17(1):116-130. doi: 10.18632/aging.206187. Epub 2025 Jan 6. Aging (Albany NY). 2025. PMID: 39773533 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Serhan CN, Hong S, Gronert K, Colgan SP, Devchand PR, Mirick G, Moussignac R-L, Resolvins: a family of bioactive products of omega-3 fatty acid transformation circuits initiated by aspirin treatment that counter proinflammation signals, J. Exp. Med 196 (2002) 1025–1037, 10.1084/jem.20020760. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

