Systematic Analysis of IL-1 Cytokine Signaling Suppression by HPV16 Oncoproteins
- PMID: 36342298
- PMCID: PMC9683014
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.01326-22
Systematic Analysis of IL-1 Cytokine Signaling Suppression by HPV16 Oncoproteins
Abstract
The human papillomavirus (HPV) E6 and E7 oncogenes are expressed at all stages of HPV-mediated carcinogenesis and are essential drivers of cancers caused by high-risk HPV. Some of the activities of HPV E6 and E7, such as their interactions with host cellular tumor suppressors, have been characterized extensively. There is less information about how high-risk HPV E6 and E7 alter cellular responses to cytokines that are present in HPV-infected tissues and are an important component of the tumor microenvironment. We used several models of HPV oncoprotein activity to assess how HPV16 E6 and E7 alter the cellular response to the proinflammatory cytokine IL-1β. Models of early stage HPV infection and of established HPV-positive head and neck cancers exhibited similar dysregulation of IL-1 pathway genes and suppressed transcriptional responses to IL-1β treatment. Such overlap in cell responses supports that changes induced by HPV16 E6 and E7 early in infection could persist and contribute to a dysregulated immune environment throughout carcinogenesis. HPV16 E6 and E7 also drove the upregulation of several suppressors of IL-1 cytokine signaling, including SIGIRR, both in primary keratinocytes and in cancer cells. SIGIRR knockout was insufficient to increase IL-1β-dependent gene expression in the presence of HPV16 E6 and E7, suggesting that multiple suppressors of IL-1 signaling contribute to dampened IL-1 responses in HPV16-positive cells. IMPORTANCE Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection is responsible for nearly 5% of the worldwide cancer burden. HPV-positive tumors develop over years to decades in tissues that are subject to frequent stimulation by proinflammatory cytokines. However, the effects of HPV oncoproteins on the cellular response to cytokine stimulation are not well defined. We analyzed IL-1 cytokine signaling in several models of HPV biology and disease. We found that HPV16 E6 and E7 oncoproteins mediate a broad and potent suppression of cellular responses to IL-1β in models of both early and late stages of carcinogenesis. Our data provide a resource for future investigation of IL-1 signaling in HPV-positive cells and cancers.
Keywords: HPV; IL-1; carcinogenesis; cell growth; cytokine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
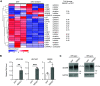
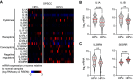
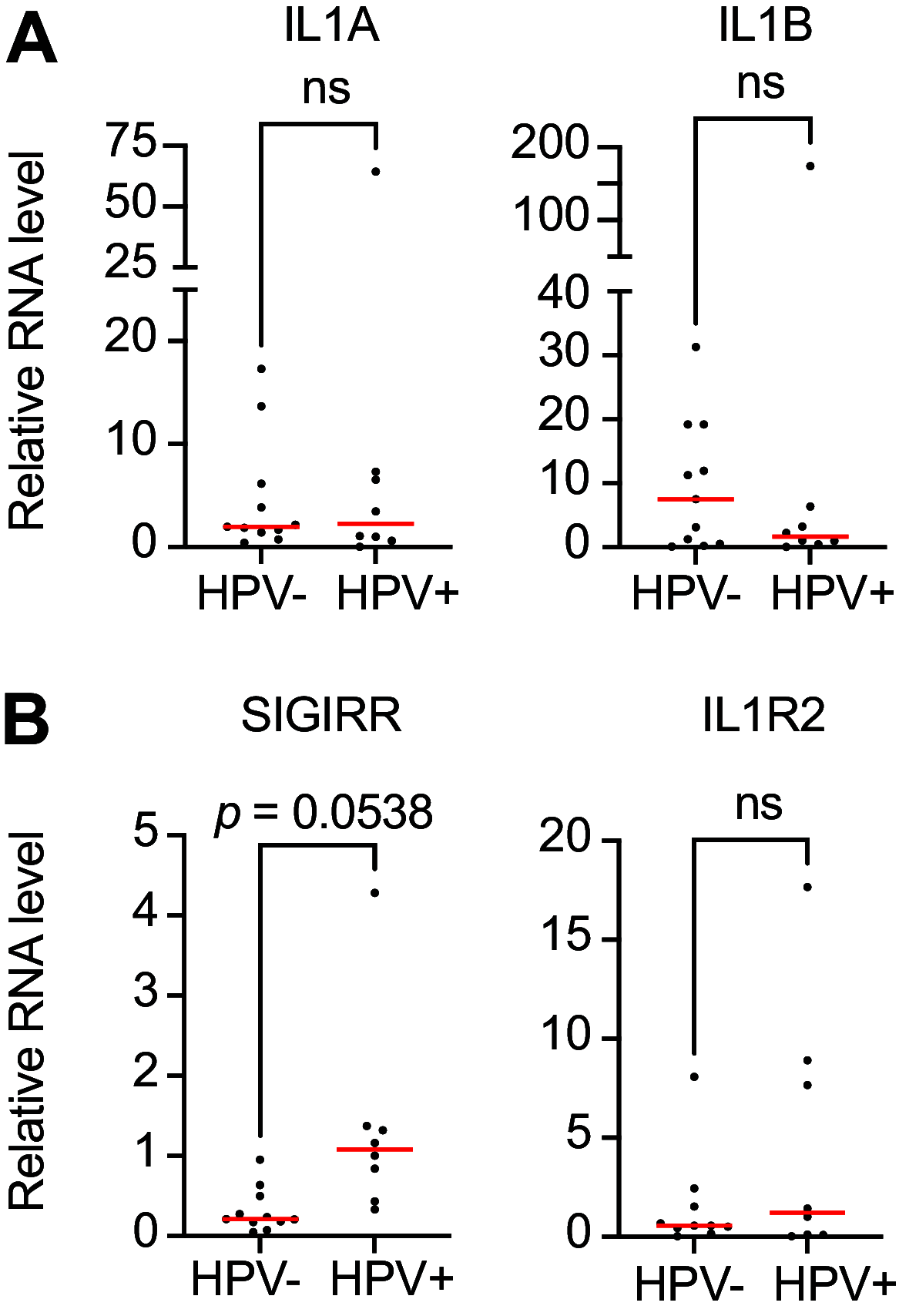




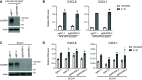
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

