Incidental Coronary Artery Calcium: Opportunistic Screening of Previous Nongated Chest Computed Tomography Scans to Improve Statin Rates (NOTIFY-1 Project)
- PMID: 36342823
- PMCID: PMC10108579
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.122.062746
Incidental Coronary Artery Calcium: Opportunistic Screening of Previous Nongated Chest Computed Tomography Scans to Improve Statin Rates (NOTIFY-1 Project)
Abstract
Background: Coronary artery calcium (CAC) can be identified on nongated chest computed tomography (CT) scans, but this finding is not consistently incorporated into care. A deep learning algorithm enables opportunistic CAC screening of nongated chest CT scans. Our objective was to evaluate the effect of notifying clinicians and patients of incidental CAC on statin initiation.
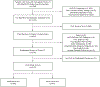
Methods: NOTIFY-1 (Incidental Coronary Calcification Quality Improvement Project) was a randomized quality improvement project in the Stanford Health Care System. Patients without known atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease or a previous statin prescription were screened for CAC on a previous nongated chest CT scan from 2014 to 2019 using a validated deep learning algorithm with radiologist confirmation. Patients with incidental CAC were randomly assigned to notification of the primary care clinician and patient versus usual care. Notification included a patient-specific image of CAC and guideline recommendations regarding statin use. The primary outcome was statin prescription within 6 months.
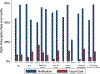
Results: Among 2113 patients who met initial clinical inclusion criteria, CAC was identified by the algorithm in 424 patients. After chart review and additional exclusions were made, a radiologist confirmed CAC among 173 of 194 patients (89.2%) who were randomly assigned to notification or usual care. At 6 months, the statin prescription rate was 51.2% (44/86) in the notification arm versus 6.9% (6/87) with usual care (P<0.001). There was also more coronary artery disease testing in the notification arm (15.1% [13/86] versus 2.3% [2/87]; P=0.008).
Conclusions: Opportunistic CAC screening of previous nongated chest CT scans followed by clinician and patient notification led to a significant increase in statin prescriptions. Further research is needed to determine whether this approach can reduce atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease events.
Registration: URL: https://www.
Clinicaltrials: gov; Unique identifier: NCT04789278.
Keywords: atherosclerosis; computed tomography angiography; coronary artery disease; electronic health record; primary prevention.
Figures
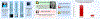
Comment in
-
Response by Sandhu et al to Letter Regarding Article, "Incidental Coronary Artery Calcium: Opportunistic Screening of Previous Nongated Chest Computed Tomography Scans to Improve Statin Rates (NOTIFY-1 Project)".Circulation. 2023 Aug;148(5):441. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.123.065360. Epub 2023 Jul 31. Circulation. 2023. PMID: 37523759 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Letter by Cainzos-Achirica Regarding Article, "Incidental Coronary Artery Calcium: Opportunistic Screening of Previous Nongated Chest Computed Tomography Scans to Improve Statin Rates (NOTIFY-1 Project)".Circulation. 2023 Aug;148(5):440. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.122.063210. Epub 2023 Jul 31. Circulation. 2023. PMID: 37523761 No abstract available.
References
-
- Tsao CW, Aday AW, Almarzooq ZI, Alonso A, Beaton AZ, Bittencourt MS, Boehme AK, Buxton AE, Carson AP, Commodore-Mensah Y, Elkind MSV, Evenson KR, Eze-Nliam C, Ferguson JF, Generoso G, Ho JE, Kalani R, Khan SS, Kissela BM, Knutson KL, Levine DA, Lewis TT, Liu J, Loop MS, Ma J, Mussolino ME, Navaneethan SD, Perak AM, Poudel R, Rezk-Hanna M, Roth GA, Schroeder EB, Shah SH, Thacker EL, VanWagner LB, Virani SS, Voecks JH, Wang NY, Yaffe K and Martin SS. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2022 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2022;145:e153–e639. - PubMed
-
- Nanna MG, Navar AM, Wang TY, Mi X, Virani SS, Louie MJ, Lee LV, Goldberg AC, Roger VL, Robinson J and Peterson ED. Statin Use and Adverse Effects Among Adults >75 Years of Age: Insights From the Patient and Provider Assessment of Lipid Management (PALM) Registry. J Am Heart Assoc. 2018. May 8;7(10):e008546. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Saeed A, Zhu J, Thoma F, Marroquin O, Aiyer A, Agarwala A, Virani SS, Gulati M, Lee JS, Reis S, Saba S, Ballantyne C and Mulukutla S. Cardiovascular Disease Risk-Based Statin Utilization and Associated Outcomes in a Primary Prevention Cohort: Insights From a Large Health Care Network. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2021;14:e007485. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

