Ultrasound Retinal Stimulation: A Mini-Review of Recent Developments
- PMID: 36343006
- PMCID: PMC10424795
- DOI: 10.1109/TUFFC.2022.3220568
Ultrasound Retinal Stimulation: A Mini-Review of Recent Developments
Abstract
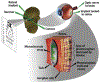
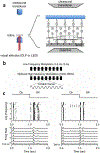
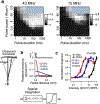
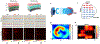
Ultrasound neuromodulation is an emerging technology. A significant amount of effort has been devoted to investigating the feasibility of noninvasive ultrasound retinal stimulation. Recent studies have shown that ultrasound can activate neurons in healthy and degenerated retinas. Specifically, high-frequency ultrasound can evoke localized neuron responses and generate patterns in visual circuits. In this review, we recapitulate pilot studies on ultrasound retinal stimulation, compare it with other neuromodulation technologies, and discuss its advantages and limitations. An overview of the opportunities and challenges to develop a noninvasive retinal prosthesis using high-frequency ultrasound is also provided.
Figures
References
-
- Wong WL, Su X, Li X, Cheung CMG, Klein R, Cheng C-Y, and Wong TY, “Global prevalence of age-related macular degeneration and disease burden projection for 2020 and 2040: a systematic review and meta-analysis,” The Lancet Global Health, vol. 2, no. 2, pp. e106–e116, 2014. - PubMed
-
- Gaillet V, Cutrone A, Artoni F, Vagni P, Pratiwi AM, Romero SA, Di Paola DL, Micera S, and Ghezzi D, “Spatially selective activation of the visual cortex via intraneural stimulation of the optic nerve,” Nature biomedical engineering, vol. 4, no. 2, pp. 181–194, 2020. - PubMed
-
- Chen X, Wang F, Fernandez E, and Roelfsema PR, “Shape perception via a high-channel-count neuroprosthesis in monkey visual cortex,” Science, vol. 370, no. 6521, pp. 1191–1196, 2020. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

