Identification of ferroptosis-related genes in syncytiotrophoblast-derived extracellular vesicles of preeclampsia
- PMID: 36343018
- PMCID: PMC9646584
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000031583
Identification of ferroptosis-related genes in syncytiotrophoblast-derived extracellular vesicles of preeclampsia
Abstract
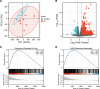
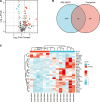
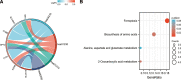
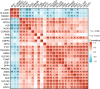
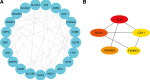
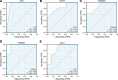
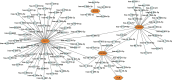
Preeclampsia (PE), defined as new-onset hypertension and multi-organ systemic complication during pregnancy, is the leading cause of maternal and neonatal mortality and morbidity. With extracellular vesicles research progresses, current data refers to the possibility that ferroptosis may play a role in exosomal effects. Evidence has suggested that ferroptosis may contribute to the pathogenesis of preeclampsia by bioinformatics analyses. The purpose of the current study is to identify the potential ferroptosis-related genes in syncytiotrophoblast-derived extracellular vesicles (STB-EVs) of preeclampsia using bioinformatics analyses. Clinical characteristics and gene expression data of all samples were obtained from the NCBI GEO database. The differentially expressed mRNAs (DE-mRNAs) in STB-EVs of preeclampsia were screened and then were intersected with ferroptosis genes. Functional and pathway enrichment analyses of ferroptosis-related DE-mRNAs in STB-EVs were performed. Ferroptosis-related hub genes in STB-EVs were identified by Cytoscape plugin CytoHubba with a Degree algorithm using a protein-protein interaction network built constructed from the STRING database. The predictive performance of ferroptosis-related hub genes was determined by a univariate analysis of receiver operating characteristic (ROC). The miRNA-hub gene regulatory network was constructed using the miRwalk database. A total of 1976 DE-mRNAs in STB-EVs were identified and the most enriched item identified by gene set enrichment analysis was signaling by G Protein-Coupled Receptors (normalized enrichment score = 1.238). These DE-mRNAs obtained 26 ferroptosis-related DE-mRNAs. Ferroptosis-related DE-mRNAs of gene ontology terms and Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathway enrichment analysis were enriched significantly in response to oxidative stress and ferroptosis. Five hub genes (ALB, NOX4, CDKN2A, TXNRD1, and CAV1) were found in the constructed protein-protein interaction network with ferroptosis-related DE-mRNAs and the areas under the ROC curves for ALB, NOX4, CDKN2A, TXNRD1, and CAV1 were 0.938 (CI: 0.815-1.000), 0.833 (CI: 0.612-1.000), 0.875 (CI: 0.704-1.000), 0.958 (CI: 0.862-1.000), and 0.854 (CI: 0.652-1.000) in univariate analysis of ROC. We constructed a regulatory network of miRNA-hub gene and the findings demonstrate that hsa-miR-26b-5p, hsa-miR-192-5p, hsa-miR-124-3p, hsa-miR-492, hsa-miR-34a-5p and hsa-miR-155-5p could regulate most hub genes. In this study, we identified several central genes closely related to ferroptosis in STB-EVs (ALB, NOX4, CDKN2A, TXNRD1, and CAV1) that are potential biomarkers related to ferroptosis in preeclampsia. Our findings will provide evidence for the involvement of ferroptosis in preeclampsia and improve the understanding of ferroptosis-related molecular pathways in the pathogenesis of preeclampsia.
Copyright © 2022 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

Similar articles
-
In silico identification and verification of ferroptosis-related genes in type 2 diabetic islets.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Aug 5;13:946492. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.946492. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35992146 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of immune-related gene signatures and immune infiltration features in early- and late-onset preeclampsia.J Gene Med. 2024 Feb;26(2):e3676. doi: 10.1002/jgm.3676. J Gene Med. 2024. PMID: 38362844
-
MicroRNA analysis of medium/large placenta extracellular vesicles in normal and preeclampsia pregnancies.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024 Apr 2;11:1371168. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1371168. eCollection 2024. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 38628314 Free PMC article.
-
Preeclampsia and syncytiotrophoblast membrane extracellular vesicles (STB-EVs).Clin Sci (Lond). 2022 Dec 22;136(24):1793-1807. doi: 10.1042/CS20220149. Clin Sci (Lond). 2022. PMID: 36511102 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular Vesicles as Biomarkers of Pregnancy Complications.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 6;25(22):11944. doi: 10.3390/ijms252211944. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39596014 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Integrated bioinformatic analysis reveals NOS2 as a novel ferroptosis-related biomarker for pre-eclampsia.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2023 Oct 10;23(1):719. doi: 10.1186/s12884-023-06051-0. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2023. PMID: 37817070 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatics Identification of Regulatory Genes and Mechanism Related to Hypoxia-Induced PD-L1 Inhibitor Resistance in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 13;24(10):8720. doi: 10.3390/ijms24108720. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37240068 Free PMC article.
-
Early prediction of pre-eclampsia using circulating placental exosomes: Newer insights.Indian J Med Res. 2023 Oct 1;158(4):385-396. doi: 10.4103/ijmr.ijmr_2143_22. Epub 2023 Sep 25. Indian J Med Res. 2023. PMID: 37987999 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enrichment of Bioactive Lipids in Urinary Extracellular Vesicles and Evidence of Apoptosis in Kidneys of Hypertensive Diabetic Cathepsin B Knockout Mice after Streptozotocin Treatment.Biomedicines. 2024 May 8;12(5):1038. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12051038. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38791000 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of potential biomarkers associated with oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of pre-eclampsia.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 Mar 7;104(10):e41784. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000041784. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 40068030 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kuklina EV, Ayala C, Callaghan WM. Hypertensive disorders and severe obstetric morbidity in the United States. Obstet Gynecol. 2009;113:1299–306. - PubMed
-
- Chappell LC, Cluver CA, Kingdom J, et al. . Pre-eclampsia. Lancet. 2021;398:341–54. - PubMed
-
- Magee LA, Nicolaides KH, von Dadelszen P. Preeclampsia. N Engl J Med. 2022;386:1817–32. - PubMed
-
- Burton GJ, Redman CW, Roberts JM, et al. . Pre-eclampsia: pathophysiology and clinical implications. BMJ. 2019;366:l2381. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

