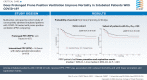
Prolonged Prone Position Ventilation Is Associated With Reduced Mortality in Intubated COVID-19 Patients
- PMID: 36343687
- PMCID: PMC9635255
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chest.2022.10.034
Prolonged Prone Position Ventilation Is Associated With Reduced Mortality in Intubated COVID-19 Patients
Abstract
Background: Prone position ventilation (PPV) is resource-intensive, yet the optimal strategy for PPV in intubated patients with COVID-19 is unclear.
Research question: Does a prolonged (24 or more h) PPV strategy improve mortality in intubated COVID-19 patients compared with intermittent (∼16 h with daily supination) PPV?
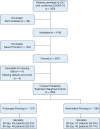
Study design and methods: Multicenter, retrospective cohort study of consecutively admitted intubated COVID-19 patients treated with PPV between March 11 and May 31, 2020. The primary outcome was 30-day all-cause mortality. Secondary outcomes included 90-day all-cause mortality and prone-related complications. Inverse probability treatment weights (IPTW) were used to control for potential treatment selection bias.
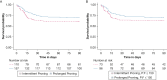
Results: Of the COVID-19 patients who received PPV, 157 underwent prolonged and 110 underwent intermittent PPV. Patients undergoing prolonged PPV had reduced 30-day (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 0.475; 95% CI, 0.336-0.670; P < .001) and 90-day (aHR, 0.638; 95% CI, 0.461-0.883; P = .006) mortality compared with intermittent PPV. In patients with Pao2/Fio2 ≤ 150 at the time of pronation, prolonged PPV was associated with reduced 30-day (aHR, 0.357; 95% CI, 0.213-0.597; P < .001) and 90-day mortality (aHR, 0.562; 95% CI, 0.357-0.884; P = .008). Patients treated with prolonged PPV underwent fewer pronation and supination events (median, 1; 95% CI, 1-2 vs 3; 95% CI, 1-4; P < .001). PPV strategy was not associated with overall PPV-related complications, although patients receiving prolonged PPV had increased rates of facial edema and lower rates of peri-proning hypotension.
Interpretation: Among intubated COVID-19 patients who received PPV, prolonged PPV was associated with reduced mortality. Prolonged PPV was associated with fewer pronation and supination events and a small increase in rates of facial edema. These findings suggest that prolonged PPV is a safe, effective strategy for mortality reduction in intubated COVID-19 patients.
Keywords: COVID-19; acute hypoxemic respiratory failure; mechanical ventilation; prone position ventilation.
Copyright © 2022 American College of Chest Physicians. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Comment in
-
Prone the Lung and Keep It Prone!Chest. 2023 Mar;163(3):469-470. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2022.12.002. Chest. 2023. PMID: 36894254 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Extended Prone Positioning Duration, But After How Many Sessions?Chest. 2023 Jun;163(6):e286-e287. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2023.02.028. Chest. 2023. PMID: 37295889 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Highlighting Prospective Data on Prolonged Prone Positioning.Chest. 2023 Jun;163(6):e290-e291. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2023.02.042. Chest. 2023. PMID: 37295894 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Kim L., Garg S., O’Halloran A., et al. Risk factors for intensive care unit admission and in-hospital mortality among hospitalized adults identified through the U.S. coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)-associated hospitalization surveillance network (COVID-NET) Clin Infect Dis. 2020 ciaa1012. - PMC - PubMed