Atrial fibrillation prediction by combining ECG markers and CMR radiomics
- PMID: 36344532
- PMCID: PMC9640662
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-21663-w
Atrial fibrillation prediction by combining ECG markers and CMR radiomics
Abstract
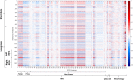
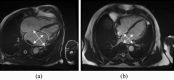
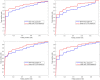
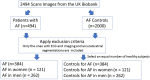
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is the most common cardiac arrhythmia. It is associated with a higher risk of important adverse health outcomes such as stroke and death. AF is linked to distinct electro-anatomic alterations. The main tool for AF diagnosis is the Electrocardiogram (ECG). However, an ECG recorded at a single time point may not detect individuals with paroxysmal AF. In this study, we developed machine learning models for discrimination of prevalent AF using a combination of image-derived radiomics phenotypes and ECG features. Thus, we characterize the phenotypes of prevalent AF in terms of ECG and imaging alterations. Moreover, we explore sex-differential remodelling by building sex-specific models. Our integrative model including radiomics and ECG together resulted in a better performance than ECG alone, particularly in women. ECG had a lower performance in women than men (AUC: 0.77 vs 0.88, p < 0.05) but adding radiomics features, the accuracy of the model was able to improve significantly. The sensitivity also increased considerably in women by adding the radiomics (0.68 vs 0.79, p < 0.05) having a higher detection of AF events. Our findings provide novel insights into AF-related electro-anatomic remodelling and its variations by sex. The integrative radiomics-ECG model also presents a potential novel approach for earlier detection of AF.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
SEP provides consultancy to and owns stock of Cardiovascular Imaging Inc, Calgary, Alberta, Canada.
Figures
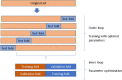
References
-
- Chugh SS, Havmoeller R, Narayanan K, Singh D, Rienstra M, Benjamin EJ, Gillum RF, Kim YH, McAnulty JH, Zheng ZJ, Forouzanfar MH, Naghavi M, Mensah GA, Ezzati M, Murray CJL. Worldwide epidemiology of atrial fibrillation: A global burden of disease 2010 study. Circulation. 2014 doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.113.005119. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hagiwara Y, Fujita H, Oh SL, Tan JH, Tan RS, Ciaccio EJ, Acharya UR. Computer-aided diagnosis of atrial fibrillation based on ECG Signals: A review. Inf. Sci. 2018 doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2018.07.063. - DOI
-
- Fuster V, Rydén LE, Cannom DS, Crijns HJ, Curtis AB, Ellenbogen KA, Halperin JL, le Heuzey J-Y, Kay GN, Lowe JE, Olsson SB, Prystowsky EN, Tamargo JL, Wann S. ACC/AHA/ESC 2006 guidelines for the management of patients with atrial fibrillation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2006 doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2006.07.018. - DOI
-
- Lip, G.Y.H., Li, F.L. & Hee, S. QJM paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- MC_UP_A620_1015/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- FS/17/81/33318/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_12011/2/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 825903/European Union's Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme
- MR/L016311/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

