Effect of FXR agonist GW4064 in the treatment of hilar cholangiocarcinoma in rats
- PMID: 36344586
- PMCID: PMC9640703
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-23539-5
Effect of FXR agonist GW4064 in the treatment of hilar cholangiocarcinoma in rats
Abstract
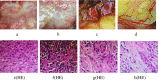
The study objective was to observe the treatment effect of the farnesoid X receptor (FXR) agonist GW4064 in a rat model of hilar cholangiocarcinoma to explore a new therapeutic target for gene therapy for hilar cholangiocarcinoma. Eighty male Wistar rats were randomly divided into four groups (treatment group, model group, control group and sham operation group, 20 rats in each group). The four groups were fed a standard diet. The treatment group and the model group were injected with a suspension of cholangiocarcinoma QBC939 cells into the hilar bile duct with a microsyringe, the control group was injected with normal saline, and the sham operation group was not injected with anything. A modified tail suspension test (TST) was used to evaluate the vitality of the rats. At 4 weeks, one rat in the treatment group and model group was euthanized, and the changes in the hilar bile duct were recorded. The procedure was repeated at 6 weeks. After 6 weeks, hilar cholangiocarcinoma occurred in the treatment group and model group. Then, the treatment group was injected with GW4064 intraperitoneally at a dose of 50 mg/kg/day. One week after injection, the rats in the four groups were euthanized. Pathological examination confirmed that tumours had formed, and hilar bile duct tissues were taken from the four groups. FXR, Bsep, Ntcp and NF-κB expression in the hilar bile duct was detected by real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and immunohistochemistry. After three weeks, the rats in the treatment group and model group ate less, and their weight was significantly reduced. Six weeks later, hilar cholangiocarcinoma was detected in the treatment group and model group. After treatment with GW4064, the ratios of FXR/GAPDH mRNA, Bsep/GAPDH mRNA, Ntcp/GAPDH mRNA and NF-κBp65/GAPDH mRNA were significantly different among the four groups. Under a light microscope, FXR protein reacted with anti-FXR antibody, Bsep protein reacted with anti-Bsep antibody, Ntcp protein reacted with anti-Ntcp antibody and NF-κBp65 protein reacted with anti-NF-κBp65 antibody, and they showed granular expression. Every pathological section included 4,800 cells, and there were different numbers of positive cells in each group. FXR expression in the hilar cholangiocarcinoma of rats was significantly lower than that in normal hilar bile duct tissues. GW4064 increased the expression of FXR in tumour tissues. These findings suggest that FXR may be a new therapeutic target and that GW4064 may be helpful in the treatment of hilar cholangiocarcinoma.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

