The relationship between structural analysis of the hand and clinical characteristics in psoriatic arthritis
- PMID: 36344592
- PMCID: PMC9640661
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-23555-5
The relationship between structural analysis of the hand and clinical characteristics in psoriatic arthritis
Abstract
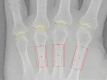
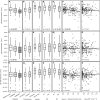
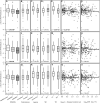
Up to now, there is only limited information available on a possible relationship between clinical characteristics and the mineralization of metacarpal bones and finger joint space distance (JSD) in patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA). Computerized digital imaging techniques like digital X-ray radiogrammetry (DXR) and computer-aided joint space analysis (CAJSA) have significantly improved the structural analysis of hand radiographs and facilitate the recognition of radiographic damage. The objective of this study was to evaluate clinical features which potentially influence periarticular mineralization of the metacarpal bones and finger JSD in PsA-patients. 201 patients with PsA underwent computerized measurements of the metacarpal bone mineral density (BMD) with DXR and JSD of all finger joints by CAJSA. DXR-BMD and JSD were compared with clinical features such as age and sex, disease duration, C-reactive protein (CRP) as well as treatment with prednisone and disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs). A longer disease duration and an elevated CRP value were associated with a significant reduction of DXR-BMD, whereas JSD-parameters were not affected by both parameters. DXR-BMD was significantly reduced in the prednisone group (-0.0383 g/cm²), but prednisone showed no impact on finger JSD. Patients under the treatment with bDMARDs presented significant lower DXR-BMD (-0.380 g/cm²), JSDMCP (-0.0179 cm), and JSDPIP (-0.0121 cm) values. Metacarpal BMD was influenced by inflammatory activity, prednisone use, and DMARDs. In contrast, finger JSD showed only a change compared to baseline therapy. Therefore, metacarpal BMD as well as finger JSD represent radiographic destruction under different aspects.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Wassenberg S. Radiographic scoring methods in psoriatic arthritis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2015;33(5 Suppl 93):S55–S59. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

