ADRA1A-Gαq signalling potentiates adipocyte thermogenesis through CKB and TNAP
- PMID: 36344764
- PMCID: PMC9684074
- DOI: 10.1038/s42255-022-00667-w
ADRA1A-Gαq signalling potentiates adipocyte thermogenesis through CKB and TNAP
Abstract
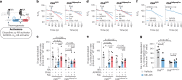
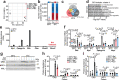
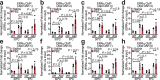
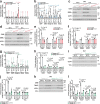
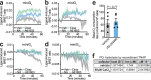
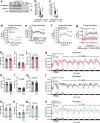
Noradrenaline (NA) regulates cold-stimulated adipocyte thermogenesis1. Aside from cAMP signalling downstream of β-adrenergic receptor activation, how NA promotes thermogenic output is still not fully understood. Here, we show that coordinated α1-adrenergic receptor (AR) and β3-AR signalling induces the expression of thermogenic genes of the futile creatine cycle2,3, and that early B cell factors, oestrogen-related receptors and PGC1α are required for this response in vivo. NA triggers physical and functional coupling between the α1-AR subtype (ADRA1A) and Gαq to promote adipocyte thermogenesis in a manner that is dependent on the effector proteins of the futile creatine cycle, creatine kinase B and tissue-non-specific alkaline phosphatase. Combined Gαq and Gαs signalling selectively in adipocytes promotes a continual rise in whole-body energy expenditure, and creatine kinase B is required for this effect. Thus, the ADRA1A-Gαq-futile creatine cycle axis is a key regulator of facultative and adaptive thermogenesis.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



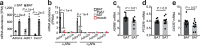




References
-
- Cannon B, Nedergaard J. Nonshivering thermogenesis and its adequate measurement in metabolic studies. J. Exp. Biol. 2011;214:242–253. - PubMed
-
- Hsieh AC, Carlson LD. Role of adrenaline and noradrenaline in chemical regulation of heat production. Am. J. Physiol. 1957;190:243–246. - PubMed
-
- Derry DM, Schonbaum E, Steiner G. Two sympathetic nerve supplies to brown adipose tissue of the rat. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 1969;47:57–63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

