A randomized clinical trial of lipid metabolism modulation with fenofibrate for acute coronavirus disease 2019
- PMID: 36344766
- PMCID: PMC9640855
- DOI: 10.1038/s42255-022-00698-3
A randomized clinical trial of lipid metabolism modulation with fenofibrate for acute coronavirus disease 2019
Abstract
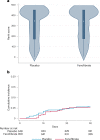
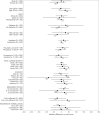
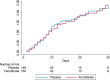
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) cytotoxicity may involve inhibition of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha. Fenofibrate activates peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha and inhibits SARS-CoV-2 replication in vitro. Whether fenofibrate can be used to treat coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection in humans remains unknown. Here, we randomly assigned inpatients and outpatients with COVID-19 within 14 d of symptom onset to 145 mg of oral fenofibrate nanocrystal formulation versus placebo for 10 d, in a double-blinded fashion. The primary endpoint was a severity score whereby participants were ranked across hierarchical tiers incorporating time to death, mechanical ventilation duration, oxygenation, hospitalization and symptom severity and duration. In total, 701 participants were randomized to fenofibrate (n = 351) or placebo (n = 350). The mean age of participants was 49 ± 16 years, 330 (47%) were female, mean body mass index was 28 ± 6 kg/m2 and 102 (15%) had diabetes. Death occurred in 41 participants. Compared with placebo, fenofibrate had no effect on the primary endpoint. The median (interquartile range) rank in the placebo arm was 347 (172, 453) versus 345 (175, 453) in the fenofibrate arm (P = 0.819). There was no difference in secondary and exploratory endpoints, including all-cause death, across arms. There were 61 (17%) adverse events in the placebo arm compared with 46 (13%) in the fenofibrate arm, with slightly higher incidence of gastrointestinal side effects in the fenofibrate group. Overall, among patients with COVID-19, fenofibrate has no significant effect on various clinically relevant outcomes ( NCT04517396 ).
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
In the last 2 years, J.B.C. has received research grants from the National Institutes of Health and American Heart Association. In the last 2 years, J.A.C. has received consulting honoraria from Sanifit, Bristol Myers Squibb, Merck, Edwards Lifesciences, Bayer, JNJ, the University of Delaware, and research grants from the National Institutes of Health, Abbott, Microsoft, Fukuda-Denshi and Bristol Myers Squibb. J.A.C. has received compensation from the American Heart Association and the American College of Cardiology for editorial roles, and visiting speaker honoraria from Washington University, University of Utah, the Japanese Association for Cardiovascular Nursing and the Korean Society of Cardiology. E.J.G. has received honoraria from Abbott CH, bioMérieux, Brahms, GSK, InflaRx, Sobi and XBiotech; independent educational grants from Abbott CH, AxisShield, bioMérieux, InflaRx, Johnson & Johnson, MSD, Sobi and XBiotech; and funding from the Horizon 2020 Marie-Curie Project European Sepsis Academy (granted to the National and Kapodistrian University of Athens), and the Horizon 2020 European Grants ImmunoSep and RISKinCOVID (granted to the Hellenic Institute for the Study of Sepsis). In the last 2 years, N.K.S. has received compensation from the American Heart Association for editorial duties. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Update of
-
A Randomized Trial of Lipid Metabolism Modulation with Fenofibrate for Acute Coronavirus Disease 2019.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2022 Aug 10:rs.3.rs-1933913. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-1933913/v1. Res Sq. 2022. Update in: Nat Metab. 2022 Dec;4(12):1847-1857. doi: 10.1038/s42255-022-00698-3. PMID: 35982675 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Oguz, S. H. & Okan Yildiz, B. Endocrine disorders and COVID-19. Annu. Rev. Med.10.1146/annurev-med-043021-033509 (2022). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

