Analgesic effects and arthritic changes following intra-articular injection of diclofenac etalhyaluronate in a rat knee osteoarthritis model
- PMID: 36344944
- PMCID: PMC9641934
- DOI: 10.1186/s12891-022-05937-y
Analgesic effects and arthritic changes following intra-articular injection of diclofenac etalhyaluronate in a rat knee osteoarthritis model
Abstract
Background: Diclofenac etalhyaluronate (DF-HA) is a recently developed analgesic conjugate of diclofenac and hyaluronic acid that has analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects on acute arthritis. In this study, we investigated its analgesic effect on osteoarthritis, using a rat model of monoiodoacetate (MIA).
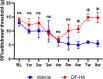
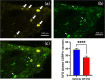
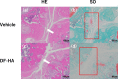
Methods: We injected MIA into the right knees of eight 6-weeks-old male Sprague-Dawley rats. Four weeks later, rats were randomly injected with DF-HA or vehicle into the right knee. Seven weeks after the MIA injection, fluorogold (FG) and sterile saline were injected into the right knees of all the rats. We assessed hyperalgesia with weekly von Frey tests for 8 weeks after MIA administration. We took the right knee computed tomography (CT) as radiographical evaluation every 2 weeks. All rats were sacrificed 8 weeks after administration of MIA for histological evaluation of the right knee and immunohistochemical evaluation of the DRG and spinal cord. We also evaluated the number of FG-labeled calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP)-immunoreactive(ir) neurons in the dorsal root ganglion (DRG) and ionized calcium-binding adapter molecule 1 (Iba1)-ir microglia in the spinal cord.
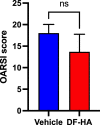
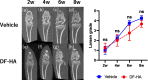
Results: Administration of DF-HA significantly improved pain sensitivity and reduced CGRP and Iba1 expression in the DRG and spinal cord, respectively. However, computed tomography and histological evaluation of the right knee showed similar levels of joint deformity, despite DF-HA administration.
Conclusion: DF-HA exerted analgesic effects on osteoarthritic pain, but did not affect joint deformity.
Keywords: Diclofenac etalhyaluronate; Osteoarthritis; Pain; Rat monoiodoacetate model.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors except J.T. declare that they have no competing interests. J.T. is an employee of Seikagaku Corporation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comparison of effects of intra-articular diclofenac etalhyaluronate and hyaluronic acid in a monoiodoacetate rat osteoarthritis model.J Orthop Res. 2025 Mar;43(3):557-566. doi: 10.1002/jor.26012. Epub 2024 Nov 11. J Orthop Res. 2025. PMID: 39528346
-
Impact of Intra-Articular Diclofenac Etalhyaluronate on Pain and Osteoarthritic Changes in Advanced and End-Stage Hip Osteoarthritis.J Orthop Res. 2025 Jul;43(7):1325-1335. doi: 10.1002/jor.26088. Epub 2025 Apr 16. J Orthop Res. 2025. PMID: 40235431
-
Analgesic Effect of Duloxetine on an Animal Model of Monosodium Iodoacetate-Induced Hip Osteoarthritis.J Orthop Res. 2020 Feb;38(2):422-430. doi: 10.1002/jor.24480. Epub 2019 Oct 2. J Orthop Res. 2020. PMID: 31538672
-
Analgesic effects and arthritic changes following tramadol administration in a rat hip osteoarthritis model.J Orthop Res. 2022 Aug;40(8):1770-1777. doi: 10.1002/jor.25208. Epub 2021 Nov 15. J Orthop Res. 2022. PMID: 34783063
-
Pain-related sensory innervation in monoiodoacetate-induced osteoarthritis in rat knees that gradually develops neuronal injury in addition to inflammatory pain.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2011 Jun 16;12:134. doi: 10.1186/1471-2474-12-134. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2011. PMID: 21679434 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Clinical and Biochemical Implications of Hyaluronic Acid in Musculoskeletal Rehabilitation: A Comprehensive Review.J Pers Med. 2023 Nov 26;13(12):1647. doi: 10.3390/jpm13121647. J Pers Med. 2023. PMID: 38138874 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Suppression of CGRP and TRPV1 Expression in Dorsal Root Ganglia of Knee Osteoarthritis Rats by Huojing Decoction via TrkA/MKK3/6/p38 Pathway.J Inflamm Res. 2024 Aug 13;17:5311-5326. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S472341. eCollection 2024. J Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 39157588 Free PMC article.
-
An Advanced Mechanically Active Osteoarthritis-on-Chip Model to Test Injectable Therapeutic Formulations: The SYN321 Case Study.Adv Healthc Mater. 2024 Dec;13(32):e2401187. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202401187. Epub 2024 Sep 24. Adv Healthc Mater. 2024. PMID: 39318108 Free PMC article.
-
Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor: mechanisms and advances in therapy.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024 Sep 18;9(1):234. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-01931-z. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024. PMID: 39289339 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alterations in DNA methylation machinery in a rat model of osteoarthritis of the hip.J Orthop Surg Res. 2024 Jun 16;19(1):357. doi: 10.1186/s13018-024-04847-0. J Orthop Surg Res. 2024. PMID: 38880910 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stoop R, Buma P, van der Kraan PM, Hollander AP, Clark Billinghurst R, Robin Poole A, et al. Differences in type II collagen degradation between peripheral and central cartilage of rat stifle joints after cranial cruciate ligament transection. Arthritis Rheum. 2000;43:2121–2131. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200009)43:9<2121::AID-ANR24>3.0.CO;2-N. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

