Peripheral Neuropathy and Vision and Hearing Impairment in US Adults With and Without Diabetes
- PMID: 36345076
- PMCID: PMC10308505
- DOI: 10.1093/aje/kwac195
Peripheral Neuropathy and Vision and Hearing Impairment in US Adults With and Without Diabetes
Abstract
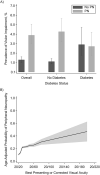
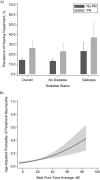
We aimed to assess the associations of peripheral neuropathy (PN) with vision and hearing impairment among adults aged ≥40 years who attended the lower-extremity disease exam for the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (United States, 1999-2004). Overall, 11.8% (standard error (SE), 0.5) of adults had diabetes, 13.2% (SE, 0.5) had PN (26.6% (SE, 1.4) with diabetes, 11.4% (SE, 0.5) without diabetes), 1.6% (SE, 0.1) had vision impairment, and 15.4% (SE, 1.1) had hearing impairment. The prevalence of vision impairment was 3.89% (95% CI: 2.99, 5.05) among adults with PN and 1.29% (95% CI: 1.04, 1.60) among adults without PN (P < 0.001). After adjustment, PN was associated with vision impairment overall (odds ratio (OR) = 1.48, 95% confidence interval (CI): 1.03, 2.13) and among adults without diabetes (OR = 1.80, 95% CI: 1.17, 2.77) but not among adults with diabetes (P for interaction = 0.018). The prevalence of hearing impairment was 26.5% (95% CI: 20.4, 33.7) among adults with PN and 14.2% (95% CI: 12.4, 16.3) among adults without PN (P < 0.001). The association of PN with moderate/severe hearing impairment was significant overall (OR = 2.55, 95% CI: 1.40, 4.64) and among adults without diabetes (OR = 3.26, 95% CI: 1.80, 5.91). Overall, these findings suggest an association between peripheral and audiovisual sensory impairment that is unrelated to diabetes.
Keywords: diabetes; hearing impairment; peripheral neuropathy.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- Dyck PJ, Litchy WJ, Lehman KA, et al. Variables influencing neuropathic endpoints: the Rochester Diabetic Neuropathy Study of Healthy Subjects. Neurology. 1995;45(6):1115–1121. - PubMed
-
- Koski K, Luukinen H, Laippala P, et al. Risk factors for major injurious falls among the home-dwelling elderly by functional abilities. A prospective population-based study. Gerontology. 1998;44(4):232–238. - PubMed
-
- Gregg EW, Gu Q, Williams D, et al. Prevalence of lower extremity diseases associated with normal glucose levels, impaired fasting glucose, and diabetes among U.S. adults aged 40 or older. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2007;77(3):485–488. - PubMed
-
- Franklin GM, Kahn LB, Baxter J, et al. Sensory neuropathy in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. The San Luis Valley Diabetes Study. Am J Epidemiol. 1990;131(4):633–643. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

