The Effect of Allograft Inflammatory Factor-1 on Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Autophagy via miR-34a/ATG4B Pathway in Diabetic Kidney Disease
- PMID: 36345369
- PMCID: PMC9637042
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/1668000
The Effect of Allograft Inflammatory Factor-1 on Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Autophagy via miR-34a/ATG4B Pathway in Diabetic Kidney Disease
Abstract
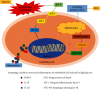
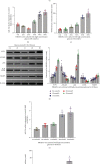
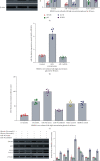
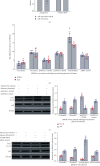
Increasing evidence suggests that disorders of inflammation, oxidative stress, and autophagy contribute to the pathogenesis of diabetic kidney disease (DKD). This study attempted to clarify the effect of allograft inflammatory factor-1 (AIF-1), miR-34a, and ATG4B on inflammation, oxidative stress, and autophagy in DKD both in vitro and in vivo experiments. In vivo, it was found that the levels of AIF-1, miR-34a, oxidative stress, and inflammatory factors were significantly increased in blood and urine samples of DKD patients and mouse models and correlated with the level of urinary protein. In vitro, it was also found that the expressions of AIF-1, miR-34a, ROS, and inflammatory factors were increased, while ATG4B and other autophagy related proteins were decreased in human renal glomerular endothelial cells (HRGECs) cultured with high concentration glucose medium (30 mmol/L). When AIF-1 gene was overexpressed, the levels of miR-34a, ROS, and inflammatory factors were significantly upregulated, and autophagy-related proteins such as ATG4B were downregulated, while downregulation of AIF-1 gene had the opposite effect. In addition, miR-34a inhibited the expression of ATG4B and autophagy-related proteins and increased the levels of ROS and inflammation. Furthermore, the result of luciferase reporter assay suggested that ATG4B was the target gene of miR-34a. When ATG4B gene was overexpressed, the level of autophagy was upregulated, and inflammatory factors were downregulated. Conversely, when ATG4B gene was inhibited, the level of autophagy was downregulated, and inflammatory factors were upregulated. Then, autophagy inducers inhibited the levels of inflammation and ROS, whereas autophagy inhibitors had the opposite function in HRGECs induced by glucose (30 mmol/L). In conclusion, the above data suggested that AIF-1 regulated the levels of inflammation, oxidative stress, and autophagy in HRGECs via miR-34a/ATG4B pathway to contribute to the pathogenesis of diabetic kidney disease.
Copyright © 2022 Hao Jianbing et al.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Allograft inflammatory factor-1 enhances inflammation and oxidative stress via the NF-κB pathway in diabetic kidney disease.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2022 Jul 23;614:63-69. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2022.04.089. Epub 2022 May 6. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2022. PMID: 35569377
-
MicroRNA-34a Inhibition Alleviates Lung Injury in Cecal Ligation and Puncture Induced Septic Mice.Front Immunol. 2020 Aug 13;11:1829. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01829. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32903604 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-34a Suppresses Autophagy in Tubular Epithelial Cells in Acute Kidney Injury.Am J Nephrol. 2015;42(2):168-75. doi: 10.1159/000439185. Epub 2015 Sep 26. Am J Nephrol. 2015. PMID: 26406385
-
Inflammation, oxidative stress, apoptosis, and autophagy in diabetes mellitus and diabetic kidney disease: the Four Horsemen of the Apocalypse.Int Urol Nephrol. 2017 May;49(5):837-844. doi: 10.1007/s11255-016-1488-4. Epub 2016 Dec 29. Int Urol Nephrol. 2017. PMID: 28035619 Review.
-
Probiotics improve renal function, glucose, lipids, inflammation and oxidative stress in diabetic kidney disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Ren Fail. 2022 Dec;44(1):862-880. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2022.2079522. Ren Fail. 2022. PMID: 35611435 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Comprehensive analysis of cuproptosis-related ceRNA network and immune infiltration in diabetic kidney disease.Heliyon. 2024 Aug 8;10(16):e35700. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35700. eCollection 2024 Aug 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39247321 Free PMC article.
-
Autophagy and its therapeutic potential in diabetic nephropathy.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Mar 20;14:1139444. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1139444. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37020591 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Yishen Tongluo formula ameliorates kidney injury modulating inflammation and apoptosis in streptozotocin-induced diabetic kidney disease mice.J Tradit Chin Med. 2025 Apr;45(2):254-265. doi: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2025.02.007. J Tradit Chin Med. 2025. PMID: 40151112 Free PMC article.
-
Physiological and pathological characteristics of vascular endothelial injury in diabetes and the regulatory mechanism of autophagy.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Jun 27;14:1191426. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1191426. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37441493 Free PMC article. Review.
-
mTOR pathway: A key player in diabetic nephropathy progression and therapeutic targets.Genes Dis. 2024 Mar 8;12(2):101260. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2024.101260. eCollection 2025 Mar. Genes Dis. 2024. PMID: 39717716 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

