An updated and comprehensive review on the ethnomedicinal uses, phytochemistry, pharmacological activity and toxicological profile of Tinospora crispa (L.) Hook. f. & Thomson
- PMID: 36345416
- PMCID: PMC9630822
- DOI: 10.1007/s11101-022-09843-y
An updated and comprehensive review on the ethnomedicinal uses, phytochemistry, pharmacological activity and toxicological profile of Tinospora crispa (L.) Hook. f. & Thomson
Abstract
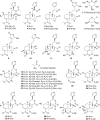
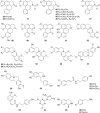
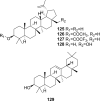
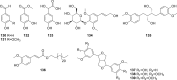
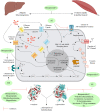
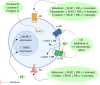
Tinospora crispa (L.) Hook. f. & Thomson (Menispermaceae) is a plant indigenous to Africa and South-East Asia. It is widely used in ethnomedicine to alleviate various diseases including hypertension, diabetes, rheumatism, jaundice, inflammation, fever, fractures, scabies, and urinary disorders. A total of 167 phytoconstituents, belonging to 12 different chemical categories, including alkaloids, flavonoids, terpenoids, and phenolic compounds have thus far been isolated from various parts of T. crispa. Numerous in vitro and in vivo investigations have already established the antidiabetic, anticancer, antiparasitic, antimicrobial, immunomodulatory, hepatoprotective, analgesic, antipyretic, antihyperuricemic, and pesticidal activity of this plant, as well as its effects on the cardiac and the central nervous system. Most pharmacological investigations to date have been carried out on plant extracts and fractions. The exact identity of the phytoconstituents responsible for the observed biological effects and their mode of action at the molecular level are yet to be ascertained. Toxicological studies have demonstrated that T. crispa is relatively safe, although dose-dependent hepatotoxicity is a concern at high doses. This review presents a comprehensive update and analysis on studies related to the ethnomedicinal uses, phytochemistry, pharmacological activity and toxicological profile of T. crispa. It provides some critical insights into the current scientific knowledge on this plant and its future potential in pharmaceutical research.
Keywords: Ethnomedicinal uses; Pharmacological activity; Phytoconstituents; Tinospora crispa; Toxicological profile.
© The Author(s) 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors have no known conflicts of interest associated with this publication and there has been no significant financial support for this work that could have influenced its outcome.
Figures







References
-
- Abdillah S, Tambunan RM, Farida Y, et al. Phytochemical screening and antimalarial activity of some plants traditionally used in Indonesia. Asian Pac J Trop Dis. 2015;5:454–457. doi: 10.1016/S2222-1808(15)60814-3. - DOI
-
- Abu MN, Hassan HF, Yusoff R, Ismail WIW. Tinospora crispa methanol crude extract activates apoptotic pathway of insulin resistant-HepG2 cell lines by improving the insulin sensitivity. Malays Appl Biol. 2017;46:145–152.
-
- Adnan AZ, Armin F, Sudji IR, et al. In vitro anti-inflammatory activity test of tinocrisposide and freeze-dried aqueous extract of Tinospora crispa stems on human red blood cell by increasing membrane stability experiment. Asian J Pharm Clin Res. 2019 doi: 10.22159/ajpcr.2019.v12i5.30690. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
