An in vivo and in vitro assessment of the anti-breast cancer activity of crude extract and fractions from Prunella vulgaris L
- PMID: 36345524
- PMCID: PMC9636486
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e11183
An in vivo and in vitro assessment of the anti-breast cancer activity of crude extract and fractions from Prunella vulgaris L
Abstract
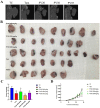
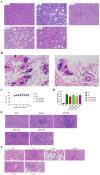
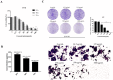
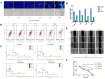
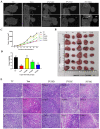
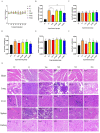
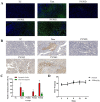
Prunella vulgaris L.(P. vulgaris) is a perennial herb belonging to the Labiate family and widely distributed in China, Japan, Korea and Europe. Medical monographs and previous studies have shown that P. vulgaris has significant anti-breast cancer activity, and its use in breast treatment has a long history. However, systematically reports about the material basis and mechanism of P. vulgaris on anti-breast cancer activity are limited. In the present study, we first screened the best active fraction from the crude extract (PVE) and ethanol eluted fractions of P. vulgaris by using MDA-MB-231, MCF-7, 4T1 cell models in vitro and a 4T1-BALB/c transplanted tumour mouse breast cancer model in vivo. Furthermore, the anti-breast cancer mechanism of the best active fraction was investigated. The results demonstrated that PVE and ethanol fractions exhibited anti-breast cancer activity, especially with the 50% ethanol eluted fraction (PV50), which effectively regulated the 4T1 cell cycle, inhibited tumour cell proliferation, and promoted cancer cell apoptosis. In case of in vivo assays, PV50 inhibited tumour growth and lung metastasis, as well as inducing cell apoptosis by promoting damage of nuclear DNA and increasing expression of cleaved caspase-3. In addition, the chemical compositions of PV50 were analyzed by HPLC and UPLC-MS/MS, which were identified as flavonoids, moderately polar triterpenes, and a small amount of phenolic acid. The PV50 could be applied as natural sources against breast cancer in the pharmaceutical industry. These findings provide a basis for understanding the mechanism of the anti-breast cancer activity of P. vulgaris.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Breast cancer; Caspase; Herb; Prunella vulgaris L..
© 2022 Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Screening out the anti-insomnia components from Prunella vulgaris L. based on plasma pharmacochemistry combined with pharmacodynamic experiments and UPLC-MS/MS analysis.J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Oct 28;279:114373. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.114373. Epub 2021 Jun 26. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34181959
-
Characterization and anti-uterine tumor effect of extract from Prunella vulgaris L.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2020 Jun 18;20(1):189. doi: 10.1186/s12906-020-02986-5. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2020. PMID: 32552673 Free PMC article.
-
Root extract of Prunella vulgaris inhibits in vitro and in vivo carcinogenesis in MCF-5 human breast carcinoma via suppression of angiogenesis, induction of apoptosis, cell cycle arrest and modulation of PI3K/AKT signalling pathway.J BUON. 2019 Mar-Apr;24(2):549-554. J BUON. 2019. PMID: 31128004
-
Prunella vulgaris: A Comprehensive Review of Chemical Constituents, Pharmacological Effects and Clinical Applications.Curr Pharm Des. 2019;25(3):359-369. doi: 10.2174/1381612825666190313121608. Curr Pharm Des. 2019. PMID: 30864498 Review.
-
Prunella vulgaris L: Critical Pharmacological, Expository Traditional Uses and Extensive Phytochemistry: A Review.Curr Drug Discov Technol. 2022;19(1):e140122191102. doi: 10.2174/1570163818666210203181542. Curr Drug Discov Technol. 2022. PMID: 33538676 Review.
Cited by
-
Nanopore analysis of salvianolic acids in herbal medicines.Nat Commun. 2024 Mar 5;15(1):1970. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-45543-1. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38443335 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Tumor Effects and Toxicity Reduction Mechanisms of Prunella vulgaris: A Comprehensive Review.Molecules. 2024 Apr 18;29(8):1843. doi: 10.3390/molecules29081843. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38675663 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combination of RNA-sequencing data analysis, network pharmacology, molecular docking techniques to investigate the mechanism of Prunella vulgaris L. in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer.Discov Oncol. 2025 May 12;16(1):726. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-02563-7. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40353950 Free PMC article.
-
An Integrated Approach of Network Pharmacology, Bioinformatics, Molecular Docking, and Experimental Verification Uncovers Prunellae Spica as the Potential Medicine of Prognosis Improvement for Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Curr Pharm Des. 2025;31(5):391-412. doi: 10.2174/0113816128328547240827045955. Curr Pharm Des. 2025. PMID: 39289945
-
Triterpenes of Prunella vulgaris Inhibit Triple-Negative Breast Cancer by Regulating PTP1B/PI3K/AKT/mTOR and IL-24/CXCL12/CXCR4 Pathways.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 24;26(5):1959. doi: 10.3390/ijms26051959. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40076586 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cohen I., Tagliaferri M., Tripathy D. Traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of breast cancer. Semin. Oncol. 2002;29:563–574. - PubMed
-
- Moran M.S. Radiation therapy in the locoregional treatment of triple-negative breast cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16(3):113–122. - PubMed
-
- Feng Y.X., Spezia M., Huang S.F., Yuan C.F., Zeng Z.Y., Zhang L.H., Ji X.J., Liu W., Huang B., Luo W.P., Liu B., Lei Y., Du S., Vuppalapati A., H Luu H., C Haydon R., He T.C., Ren G.S. Breast cancer development and progression: risk factors, cancer stem cells, signaling pathways, genomics, and molecular pathogenesis. Genes Dis. 2018;5(2):77–106. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tao M., Ma D.L., Li Y., Zhou C., Li Y., Zhang Y.S., Duan W.M., Xu X.J., Wang R., Wu L.Z., Liu H.Y. Clinical significance of circulating tumor cells in breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2011;129(1):247–254. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

