Characterization of Viruses in Phase 3 and Phase 3b Trials (the Ring Study and the Dapivirine Ring Extended Access and Monitoring Trial) of the Dapivirine Vaginal Ring for Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Infection Risk Reduction
- PMID: 36345569
- PMCID: PMC12097997
- DOI: 10.1093/cid/ciac875
Characterization of Viruses in Phase 3 and Phase 3b Trials (the Ring Study and the Dapivirine Ring Extended Access and Monitoring Trial) of the Dapivirine Vaginal Ring for Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Infection Risk Reduction
Abstract
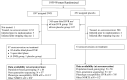
Background: The Ring Study demonstrated 35.1% human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) infection risk reduction among participants who used the Dapivirine vaginal ring-004 (DVR), whereas the Dapivirine Ring Extended Access and Monitoring (DREAM) trial, approximated a 62% risk reduction. The observed non-nucleoside reverse-transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI) resistance-associated mutations (RAMs) and effects on viral susceptibility are described here.
Methods: Population-based genotyping on plasma samples collected longitudinally, and next-generation sequencing (NGS) and phenotypic susceptibility testing were done on plasma collected at seroconversion. Retrospective HIV-1 RNA testing was used to more accurately establish the time of infection.
Results: In the Ring Study, NNRTI RAMs were not observed in most viruses at seroconversion (population-based genotyping: DVR: 71 of 84, 84.5%; placebo: 50 of 58, 86.2%). However, more E138A was found in the DVR group (E138A DVR: 9 of 84, 10.7%; placebo: 2 of 58, 3.4%; P = .2, Fisher exact test). NGS detected 1 additional mutation in each group (DVR: G190A; placebo: G190A and G190E). Marginal dapivirine susceptibility reduction was found with NNRTI RAMs at seroconversion (geometric mean fold-change, range: DVR, 3.1, 1.3-5.1; placebo, 5.8, 0.9-120). NNRTI RAMs were not emergent between first detectable HIV-1 RNA and seroconversion when these visits differed (paired samples, mean ring use: DVR, n = 52, 35 days; placebo, n = 26, 31 days). After stopping DVR, 2 of 63 viruses had emergent G190G/A or K103K/N with V106V/M at final study visit. Resistance profiles from the DREAM trial were consistent with the Ring Study.
Conclusions: DVR showed little potential for selection of NNRTI-resistant variants.
Clinical trials registration: NCT01539226 and NCT02862171.
Keywords: Dapivirine vaginal ring-004; HIV-1; antiretroviral drug susceptibility; preexposure prophylaxis.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Infectious Diseases Society of America. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- European Medicines Agency . Summary of product characteristics—dapivirine vaginal ring. Available at: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/outside-eu-product-information/da.... Accessed 28 June 2022.
-
- Das K, Lewi PJ, Hughes SH, Arnold E. Crystallography and the design of anti-AIDS drugs: conformational flexibility and positional adaptability are important in the design of non-nucleoside HIV-1 reverse transcriptase inhibitors. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 2005; 88:209–31. - PubMed
-
- Nel A, van Niekerk N, Kapiga S, et al. Safety and efficacy of a dapivirine vaginal ring for HIV prevention in women. N Engl J Med 2016; 375:2133–43. - PubMed
-
- Roberts NA, Craig JC, Sheldon J. Resistance and cross-resistance with saquinavir and other HIV protease inhibitors: theory and practice. AIDS 1998; 12:453–60. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

