Protective effect of methotrexate on lung function and mortality in rheumatoid arthritis-related interstitial lung disease: a retrospective cohort study
- PMID: 36346076
- PMCID: PMC9647291
- DOI: 10.1177/17534666221135314
Protective effect of methotrexate on lung function and mortality in rheumatoid arthritis-related interstitial lung disease: a retrospective cohort study
Abstract
Background: Studies on the risk and protective factors for lung function decline and mortality in rheumatoid arthritis-related interstitial lung disease (RA-ILD) are limited.
Objectives: We aimed to investigate clinical factors and medication uses associated with lung function decline and mortality in RA-ILD.
Methods: This retrospective cohort study examined the medical records of patients with RA-ILD who visited Severance Hospital between January 2006 and December 2019. We selected 170 patients with RA-ILD who had undergone at least one spirometry test and chest computed tomography scan. An absolute decline of ⩾10% in the functional vital capacity (FVC) was defined as significant decline in pulmonary function. Data for analysis were retrieved from electronic medical records.
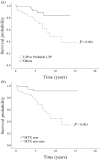
Results: Ninety patients (52.9%) were female; the mean age was 64.0 ± 10.2 years. Multivariate logistic regression showed that a high erythrocyte sediment rate level at baseline [odds ratio (OR) = 3.056; 95% confidence interval (CI) = 1.183-7.890] and methotrexate (MTX) use (OR = 0.269; 95% CI = 0.094-0.769) were risk and protective factors for lung function decline, respectively. Multivariate Cox regression analysis indicated that age ⩾65 years (OR = 2.723; 95% CI = 1.142-6.491), radiologic pattern of usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP) or probable UIP (OR = 3.948; 95% CI = 1.522-10.242), baseline functional vital capacity (FVC) % predicted (OR = 0.971; 95% CI = 0.948-0.994), and MTX use (OR = 0.284; 95% CI = 0.091-0.880) were predictive of mortality.
Conclusion: We identified risk and protective factors for lung function decline and mortality in patients with RA-ILD. MTX use was associated with favorable outcome in terms of both lung function and mortality in our cohort.
Keywords: interstitial lung disease; methotrexate; mortality; pulmonary function; rheumatoid arthritis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Incidence, risk factors, and prognosis of acute exacerbation of rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Pulm Med. 2023 Jul 11;23(1):255. doi: 10.1186/s12890-023-02532-2. BMC Pulm Med. 2023. PMID: 37434169 Free PMC article.
-
Risk factors for the progression of rheumatoid arthritis-related interstitial lung disease: Clinical features, biomarkers, and treatment options.Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2022 Aug;55:152004. doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2022.152004. Epub 2022 Apr 11. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2022. PMID: 35472663
-
Rheumatoid arthritis-related interstitial lung disease (RA-ILD): methotrexate and the severity of lung disease are associated to prognosis.Clin Rheumatol. 2017 Jul;36(7):1493-1500. doi: 10.1007/s10067-017-3707-5. Epub 2017 Jun 6. Clin Rheumatol. 2017. PMID: 28585060
-
Treatment Outcomes for Rheumatoid Arthritis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease: A Real-World, Multisite Study of the Impact of Immunosuppression on Pulmonary Function Trajectory.Chest. 2023 Apr;163(4):861-869. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2022.11.035. Epub 2022 Dec 5. Chest. 2023. PMID: 36470416 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Impact of the pattern of interstitial lung disease on mortality in rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic literature review and meta-analysis.Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2019 Dec;49(3):358-365. doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2019.04.005. Epub 2019 May 15. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2019. PMID: 31153706
Cited by
-
Forced vital capacity trajectories and risk of lung transplant and ILD-related mortality among patients with rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease.Clin Rheumatol. 2024 Aug;43(8):2453-2466. doi: 10.1007/s10067-024-07028-w. Epub 2024 Jun 19. Clin Rheumatol. 2024. PMID: 38898318 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Course of Interstitial Lung Disease in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis.ACR Open Rheumatol. 2024 Dec;6(12):836-845. doi: 10.1002/acr2.11736. Epub 2024 Sep 7. ACR Open Rheumatol. 2024. PMID: 39243209 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Design of ANCHOR-RA: a multi-national cross-sectional study on screening for interstitial lung disease in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.BMC Rheumatol. 2024 May 21;8(1):19. doi: 10.1186/s41927-024-00389-4. BMC Rheumatol. 2024. PMID: 38773593 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of abatacept versus conventional synthetic disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs on rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease.Korean J Intern Med. 2024 Sep;39(5):855-864. doi: 10.3904/kjim.2023.207. Epub 2024 Aug 30. Korean J Intern Med. 2024. PMID: 39252490 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of DMARD treatment and systemic inflammation on all-cause mortality in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and interstitial lung disease: a cohort study from the German RABBIT register.RMD Open. 2024 Apr 4;10(2):e003789. doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2023-003789. RMD Open. 2024. PMID: 38580343 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

