Free-breathing 2D radial cine MRI with respiratory auto-calibrated motion correction (RAMCO)
- PMID: 36346081
- PMCID: PMC10100319
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.29499
Free-breathing 2D radial cine MRI with respiratory auto-calibrated motion correction (RAMCO)
Abstract
Purpose: To develop a free-breathing (FB) 2D radial balanced steady-state free precession cine cardiac MRI method with 100% respiratory gating efficiency using respiratory auto-calibrated motion correction (RAMCO) based on a motion-sensing camera.
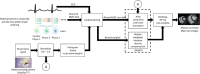
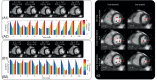
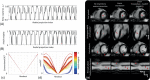
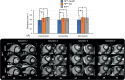
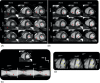
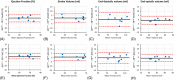
Methods: The signal from a respiratory motion-sensing camera was recorded during a FB retrospectively electrocardiogram triggered 2D radial balanced steady-state free precession acquisition using pseudo-tiny-golden-angle ordering. With RAMCO, for each acquisition the respiratory signal was retrospectively auto-calibrated by applying different linear translations, using the resulting in-plane image sharpness as a criterium. The auto-calibration determines the optimal magnitude of the linear translations for each of the in-plane directions to minimize motion blurring caused by bulk respiratory motion. Additionally, motion-weighted density compensation was applied during radial gridding to minimize through-plane and non-bulk motion blurring. Left ventricular functional parameters and sharpness scores of FB radial cine were compared with and without RAMCO, and additionally with conventional breath-hold Cartesian cine on 9 volunteers.
Results: FB radial cine with RAMCO had similar sharpness scores as conventional breath-hold Cartesian cine and the left ventricular functional parameters agreed. For FB radial cine, RAMCO reduced respiratory motion artifacts with a statistically significant difference in sharpness scores (P < 0.05) compared to reconstructions without motion correction.
Conclusion: 2D radial cine imaging with RAMCO allows evaluation of left ventricular functional parameters in FB with 100% respiratory efficiency. It eliminates the need for breath-holds, which is especially valuable for patients with no or impaired breath-holding capacity. Validation of the proposed method on patients is warranted.
Keywords: Cardiac MRI; Free-breathing Cine; Non-cartesian acquisition; respiratroy motion correction.
© 2022 The Authors. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
Guruprasad Krishnamoorthy, Jouke Smink, Marc Kouwenhoven, and Marcel Breeuwer are employees of Philips healthcare.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Two-dimensional XD-GRASP provides better image quality than conventional 2D cardiac cine MRI for patients who cannot suspend respiration.MAGMA. 2018 Feb;31(1):49-59. doi: 10.1007/s10334-017-0655-7. Epub 2017 Oct 24. MAGMA. 2018. PMID: 29067539 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Evaluation of Free-Breathing Contrast-Enhanced T1w MRI of the Liver using Pseudo Golden Angle Radial k-Space Sampling.Rofo. 2018 Jul;190(7):601-609. doi: 10.1055/s-0044-101263. Epub 2018 Mar 13. Rofo. 2018. PMID: 29534252 Clinical Trial. English.
-
3D self-gated cardiac cine imaging at 3 Tesla using stack-of-stars bSSFP with tiny golden angles and compressed sensing.Magn Reson Med. 2019 May;81(5):3234-3244. doi: 10.1002/mrm.27612. Epub 2018 Nov 25. Magn Reson Med. 2019. PMID: 30474151
-
Sorted Golden-step phase encoding: an improved Golden-step imaging technique for cardiac and respiratory self-gated cine cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging.J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2019 Apr 18;21(1):23. doi: 10.1186/s12968-019-0533-8. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2019. PMID: 30999911 Free PMC article.
-
Free-Running Cardiac and Respiratory Motion-Resolved Imaging: A Paradigm Shift for Managing Motion in Cardiac MRI?Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Sep 3;14(17):1946. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14171946. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39272732 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Free-running isotropic three-dimensional cine magnetic resonance imaging with deep learning image reconstruction.Pediatr Radiol. 2025 May 29. doi: 10.1007/s00247-025-06266-7. Online ahead of print. Pediatr Radiol. 2025. PMID: 40442341
References
-
- Utz JA, Herfkens RJ, Heinsimer JA, et al. Cine MR determination of left ventricular ejection fraction. Am J Roentgenol. 1987;148:839‐843. - PubMed
-
- Sakuma H, Fujita N, Foo TK, et al. Evaluation of left ventricular volume and mass with breath‐hold cine MR imaging. Radiology. 1993;188:377‐380. - PubMed
-
- Finn JP, Nael K, Deshpande V, Ratib O, Laub G. Cardiac MR imaging: state of the technology. Radiology. 2006;241:338‐354. - PubMed
-
- Scheffler K, Lehnhardt S. Principles and applications of balanced SSFP techniques. Eur Radiol. 2003;13:2409‐2418. - PubMed
-
- Achenbach S, Jahnke C, Paetsch I, Achenbach S. Coronary MR imaging: breath‐hold capability and patterns, coronary artery rest periods, and β‐blocker use. Radiology. 2006;239:71‐78. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

