A Low-Cost Handheld Impedimetric Biosensing System for Rapid Diagnostics of SARS-CoV-2 Infections
- PMID: 36346096
- PMCID: PMC9454264
- DOI: 10.1109/JSEN.2022.3181580
A Low-Cost Handheld Impedimetric Biosensing System for Rapid Diagnostics of SARS-CoV-2 Infections
Abstract
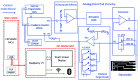
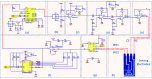
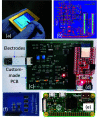
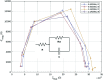
Current laboratory diagnostic approaches for virus detection give reliable results, but they require a lengthy procedure, trained personnel, and expensive equipment and reagents; hence, they are not a suitable choice for home monitoring purposes. This paper addresses this challenge by developing a portable impedimetric biosensing system for the identification of COVID-19 patients. This sensing system has two main parts: a throwaway two-working electrode (2-WE) strip and a novel read-out circuit, specifically designed for simultaneous signal acquisition from both working electrodes. Highly reliable electrochemical signal tracking from multiplex immunosensors provides a potential for flexible and portable multi-biomarker detection. The electrodes' surfaces were functionalized with SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Antibody enabling the selective detection of Nucleocapsid protein (N-protein) along with self-validation in the clinical nasopharyngeal swab specimens. The proposed programmable highly sensitive impedance read-out system allows for a wide dynamic detection range, which makes the sensor capable of detecting N-protein concentrations between 0.116 and 10,000 pg/mL. This lightweight and economical read-out arrangement is an ideal prospect for being mass-produced, especially during urgent pandemic situations. Also, such an impedimetric sensing platform has the potential to be redesigned for targeting not only other infectious diseases but also other critical disorders.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; biosensor; dual electronic read-out system; impedance measurement.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A compact, low-cost, and binary sensing (BiSense) platform for noise-free and self-validated impedimetric detection of COVID-19 infected patients.Biosens Bioelectron. 2022 Oct 1;213:114459. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2022.114459. Epub 2022 Jun 14. Biosens Bioelectron. 2022. PMID: 35728365 Free PMC article.
-
Bi-ECDAQ: An electrochemical dual-immuno-biosensor accompanied by a customized bi-potentiostat for clinical detection of SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid proteins.Biosens Bioelectron. 2022 May 1;203:114018. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2022.114018. Epub 2022 Jan 25. Biosens Bioelectron. 2022. PMID: 35114466 Free PMC article.
-
Voltammetric-based immunosensor for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid antigen.Mikrochim Acta. 2021 May 26;188(6):199. doi: 10.1007/s00604-021-04867-1. Mikrochim Acta. 2021. PMID: 34041585 Free PMC article.
-
A review on impedimetric immunosensors for pathogen and biomarker detection.Med Microbiol Immunol. 2020 Jun;209(3):343-362. doi: 10.1007/s00430-020-00668-0. Epub 2020 Apr 3. Med Microbiol Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32246198 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Utilizing Electrochemical-Based Sensing Approaches for the Detection of SARS-CoV-2 in Clinical Samples: A Review.Biosensors (Basel). 2022 Jun 29;12(7):473. doi: 10.3390/bios12070473. Biosensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35884276 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- WHO Director-General's Opening Remarks at the Media Briefing on COVID-19—16 March 2020. Accessed: Apr. 13, 2022. [Online]. Available: https://www.who.int/director-general/speeches/detail/who-director-genera...
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
