A novel selective spleen tyrosine kinase inhibitor SKI-O-703 (cevidoplenib) ameliorates lupus nephritis and serum-induced arthritis in murine models
- PMID: 36346114
- PMCID: PMC9993459
- DOI: 10.1093/cei/uxac096
A novel selective spleen tyrosine kinase inhibitor SKI-O-703 (cevidoplenib) ameliorates lupus nephritis and serum-induced arthritis in murine models
Abstract
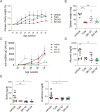
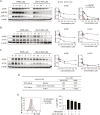
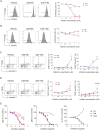
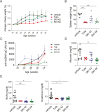
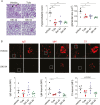
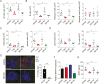
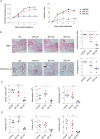
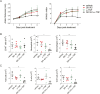
Spleen tyrosine kinase (Syk) plays a pivotal role in the activation of B cells and innate inflammatory cells by transducing immune receptor-triggered signals. Dysregulated activity of Syk is implicated in the development of antibody-mediated autoimmune diseases including systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and rheumatoid arthritis, but the effect of Syk inhibition on such diseases remains to be fully evaluated. We have developed a novel selective Syk inhibitor, SKI-O-592, and its orally bioavailable salt form, SKI-O-703 (cevidoplenib). To examine the efficacy of SKI-O-703 on the progression of SLE, New Zealand black/white mice at the autoimmunity-established phase were administrated orally with SKI-O-703 for 16 weeks. Levels of IgG autoantibody, proteinuria, and glomerulonephritis fell significantly, and this was associated with hypoactivation of follicular B cells via the germinal center. In a model of serum-transferred arthritis, SKI-O-703 significantly ameliorated synovitis, with fewer neutrophils and macrophages infiltrated into the synovial tissue. This effect was recapitulated when mice otherwise refractory to anti-TNF therapy were treated by TNF blockade combined with a suboptimal dose of SKI-O-703. These results demonstrate that the novel selective Syk inhibitor SKI-O-703 attenuates the progression of autoantibody-mediated autoimmune diseases by inhibiting both autoantibody-producing and autoantibody-sensing cells.
Keywords: Syk inhibitor SKI-O-703; autoimmune disease; spleen tyrosine kinase; systemic lupus erythematosus.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Society for Immunology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Selective inhibition of spleen tyrosine kinase (SYK) with a novel orally bioavailable small molecule inhibitor, RO9021, impinges on various innate and adaptive immune responses: implications for SYK inhibitors in autoimmune disease therapy.Arthritis Res Ther. 2013 Oct 4;15(5):R146. doi: 10.1186/ar4329. Arthritis Res Ther. 2013. PMID: 24286216 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the mechanism of action of lanraplenib, a novel spleen tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in models of lupus nephritis.BMC Rheumatol. 2021 Mar 30;5(1):15. doi: 10.1186/s41927-021-00178-3. BMC Rheumatol. 2021. PMID: 33781343 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal Structures of Spleen Tyrosine Kinase in Complex with Two Novel 4-Aminopyrido[4,3-d] Pyrimidine Derivative Inhibitors.Mol Cells. 2018 Jun;41(6):545-552. doi: 10.14348/molcells.2018.2219. Epub 2018 Jun 12. Mol Cells. 2018. PMID: 29890824 Free PMC article.
-
The role of organ-deposited IgG in the pathogenesis of multi-organ and tissue damage in systemic lupus erythematosus.Front Immunol. 2022 Oct 13;13:924766. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.924766. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36311714 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Involvement of Syk in pathology of systemic autoimmune disease].Nihon Rinsho Meneki Gakkai Kaishi. 2012;35(1):56-61. doi: 10.2177/jsci.35.56. Nihon Rinsho Meneki Gakkai Kaishi. 2012. PMID: 22374444 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Targeting B and T Lymphocyte Attenuator Regulates Lupus Disease Development in NZB/W Mice.Immunotargets Ther. 2025 Jan 17;14:7-23. doi: 10.2147/ITT.S490573. eCollection 2025. Immunotargets Ther. 2025. PMID: 39845702 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted Small Molecules for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Drugs in the Pipeline.Drugs. 2023 Apr;83(6):479-496. doi: 10.1007/s40265-023-01856-x. Epub 2023 Mar 27. Drugs. 2023. PMID: 36972009 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of Sovleplenib, a Selective Inhibitor of Syk in Clinical Development for Autoimmune Diseases and Cancers.ACS Med Chem Lett. 2024 Apr 18;15(5):595-601. doi: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.3c00553. eCollection 2024 May 9. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2024. PMID: 38746892 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

